Quasispecies and its impact on viral hepatitis
- PMID: 17349710
- PMCID: PMC7125676
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.02.001
Quasispecies and its impact on viral hepatitis
Abstract
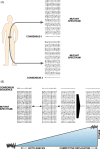
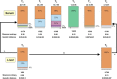
Quasispecies dynamics mediates adaptability of RNA viruses through a number of mechanisms reviewed in the present article, with emphasis on the medical implications for the hepatitis viruses. We discuss replicative and non-replicative molecular mechanisms of genome variation, modulating effects of mutant spectra, and several modes of viral evolution that can affect viral pathogenesis. Relevant evolutionary events include the generation of minority virus variants with altered functional properties, and alterations of mutant spectrum complexity that can affect disease progression or response to treatment. The widespread occurrence of resistance to antiviral drugs encourages new strategies to control hepatic viral disease such as combination therapies and lethal mutagenesis. In particular, ribavirin may be exerting in some cases its antiviral activity with participation of its mutagenic action. Despite many unanswered questions, here we document that quasispecies dynamics has provided an interpretation of the adaptability of the hepatitis viruses, with features conceptually similar to those observed with other RNA viruses, a reflection of the common underlying Darwinian principles.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resistance of high fitness hepatitis C virus to lethal mutagenesis.Virology. 2018 Oct;523:100-109. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2018.07.030. Epub 2018 Aug 11. Virology. 2018. PMID: 30107298
-
Deep sequencing in the management of hepatitis virus infections.Virus Res. 2017 Jul 15;239:115-125. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.12.020. Epub 2016 Dec 28. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 28040474 Review.
-
Ribavirin and lethal mutagenesis of poliovirus: molecular mechanisms, resistance and biological implications.Virus Res. 2005 Feb;107(2):173-81. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2004.11.007. Virus Res. 2005. PMID: 15649563 Review.
-
Viral quasispecies evolution.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012 Jun;76(2):159-216. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.05023-11. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22688811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quasispecies, error catastrophe, and the antiviral activity of ribavirin.Virology. 2002 Jul 5;298(2):175-80. doi: 10.1006/viro.2002.1487. Virology. 2002. PMID: 12127780 Review.
Cited by
-
Low host immune pressure may be associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma: a longitudinal analysis of complete genomes of the HBV 1762T, 1764A mutant.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 23;13:1214423. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1214423. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37681020 Free PMC article.
-
Deep sequencing analysis of quasispecies in the HBV pre-S region and its association with hepatocellular carcinoma.J Gastroenterol. 2017 Sep;52(9):1064-1074. doi: 10.1007/s00535-017-1334-1. Epub 2017 Mar 28. J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28353014
-
The Amino Acid Substitution Q65H in the 2C Protein of Swine Vesicular Disease Virus Confers Resistance to Golgi Disrupting Drugs.Front Microbiol. 2016 Apr 27;7:612. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00612. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27199941 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-HCV RNA Aptamers Targeting the Genomic cis-Acting Replication Element.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2011 Dec 28;5(1):49-60. doi: 10.3390/ph5010049. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2011. PMID: 24288042 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison and Correlation of Genetic Variability of the HBV Pre-S Region in HIV/HBV Co-Infected Patients: Quasispecies Perspective.Infect Drug Resist. 2020 Dec 1;13:4327-4334. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S278415. eCollection 2020. Infect Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 33293836 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe K., Inchauspe G., Fujisawa K. Genomic characterization and mutation rate of hepatitis C virus isolated from a patient who contracted hepatitis during an epidemic of non-A, non-B hepatitis in Japan. J. Gen. Virol. 1992;73:2725–2729. - PubMed
-
- Agol V.I. Molecular mechanisms of poliovirus variation and evolution. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2006;299:211–259. - PubMed
-
- Airaksinen A., Pariente N., Menendez-Arias L., Domingo E. Curing of foot-and-mouth disease virus from persistently infected cells by ribavirin involves enhanced mutagenesis. Virology. 2003;311(2):339–349. - PubMed
-
- Allen M.I., Deslauriers M., Andrews C.W., Tipples G.A., Walters K.A., Tyrrell D.L., Brown N., Condreay L.D. Identification and characterization of mutations in hepatitis B virus resistant to lamivudine. Lamivudine Clinical Investigation Group. Hepatology. 1998;27(6):1670–1677. - PubMed
-
- Anderson J.P., Daifuku R., Loeb L.A. Viral error catastrophe by mutagenic nucleosides. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2004;58:183–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

