Evidence that ATP or a related purine is an excitatory neurotransmitter in the longitudinal muscle of mouse distal colon
- PMID: 17351663
- PMCID: PMC2012975
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707188
Evidence that ATP or a related purine is an excitatory neurotransmitter in the longitudinal muscle of mouse distal colon
Abstract
Background and purpose: This study analysed the contribution of the purinergic system to enteric neurotransmission in the longitudinal muscle of mouse distal colon.
Experimental approach: Motor responses to exogenous ATP and to nerve stimulation in vitro were assessed as changes in isometric tension.
Key results: ATP induced a concentration-dependent contraction, reduced by 4-[[4-formyl-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-3-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]-2-pyridinyl]azo]-1,3-benzene disulphonic acid (PPADS), suramin, P2Y purinoreceptor desensitisation with adenosine 5'-O-2-thiodiphosphate (ADPbetaS), and atropine, but unaffected by P2X purinoceptor desensitisation with alpha,beta-methylene ATP (alpha,beta-meATP) and by 2,2-dimethyl-propionic acid 3-(2-chloro-6-methylaminopurin-9-yl)-2-(2,2-dimethyl-propionyloxymethyl)-propyl ester (MRS 2395), a P2Y(12) selective antagonist. The response to ATP was increased by 2'-deoxy-N(6)-methyl adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate (MRS 2179), a P2Y(1) selective antagonist, tetrodotoxin (TTX) or N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME). ADPbetaS, a P2Y-purinergic agonist, induced muscular contraction, with the same pharmacological profile as the ATP-induced contraction. ADP, a natural ligand for P2Y(1) receptors, induced muscular relaxation, antagonized by MRS 2179 and by TTX or L-NAME. Nerve stimulation elicited a transient nitrergic relaxation, followed by contraction. Contractile responses was reduced by atropine, PPADS, suramin, P2Y purinoceptor desensitisation, but not by P2X purinoceptor desensitisation, MRS 2179 or MRS 2395. None of the purinergic antagonists modified the nerve-evoked relaxation.
Conclusions and implications: In the longitudinal muscle of mouse distal colon, ATP, through ADPbetaS-sensitive P2Y purinoceptors, contributed to the excitatory neurotransmission acting directly on smooth muscle and indirectly via activation of cholinergic neurons. Moreover, P2Y1 purinoceptors appear to be located on nitrergic inhibitory neurons. This study provides new insights into the role of purines in the mechanism inducing intestinal transit in mouse colon.
Figures
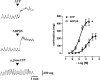
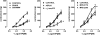

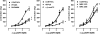
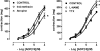

Similar articles
-
Inhibitory purinergic transmission in mouse caecum: role for P2Y1 receptors as prejunctional modulators of ATP release.Neuroscience. 2007 Dec 12;150(3):658-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.09.055. Epub 2007 Sep 29. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17997228
-
Activation of P2Y receptors by ATP and by its analogue, ADPbetaS, triggers two calcium signal pathways in the longitudinal muscle of mouse distal colon.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Oct 24;595(1-3):84-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.07.057. Epub 2008 Aug 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18713670
-
Pharmacological evidence for the existence of multiple P2 receptors in the circular muscle of guinea-pig colon.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Jan;123(1):122-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701558. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9484862 Free PMC article.
-
Dual control of local blood flow by purines.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:31-44; discussion 44-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37659.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990. PMID: 2291529 Review.
-
Overview. Purinergic mechanisms.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:1-17; discussion 18. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37657.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990. PMID: 1981306 Review.
Cited by
-
A holistic view of adenosine in the control of intestinal neuromuscular functions: the enteric 'purinome' concept.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Nov;164(6):1577-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01529.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21658024 Free PMC article.
-
Ibogaine-Mediated ROS/Antioxidant Elevation in Isolated Rat Uterus Is β-Adrenergic Receptors and KATP Channels Mediated.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Nov 9;10(11):1792. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111792. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829663 Free PMC article.
-
Garcinia buchananii stem bark extract and its bioactive constituents manniflavanone, GB-2 and buchananiflavanone attenuate intestinal inhibitory neuromuscular transmission.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2023;59:34-57. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.59.34. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2023. PMID: 37407438 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Role of Alarmins in Food Allergy: An Update on Pathophysiological Insights, Potential Use as Disease Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Implications.J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 4;12(7):2699. doi: 10.3390/jcm12072699. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37048784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Satellite glial cell P2Y12 receptor in the trigeminal ganglion is involved in lingual neuropathic pain mechanisms in rats.Mol Pain. 2012 Mar 30;8:23. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-8-23. Mol Pain. 2012. PMID: 22458630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G. Purinoceptors: are there families of P2X and P2Y purinoceptors. Pharmacol Ther. 1994;64:445–475. - PubMed
-
- Barthó L, Undi S, Benko R, Wolf M, Lazar Z, Lenard L, Jr, et al. Multiple motor effects of ATP and their inhibition by P purinoceptor antagonist, pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2',4'-disulphonic acid in the small intestine of the guinea-pig. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2006;98:488–495. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G.Purinergic signalling in gut Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology 2001Springer: Berlin; In: Abbracchio MP, Williams M (eds)vol. 151/II Purinergic and Pyrimidinergic Signalling II Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Immune, Metabolic and Gastrointestinal Tract Function
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

