Fatigue: an important feature of late-onset Pompe disease
- PMID: 17351726
- PMCID: PMC2779379
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-006-0434-2
Fatigue: an important feature of late-onset Pompe disease
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the prevalence and severity of fatigue in adult patients with Pompe disease.
Methods: The Fatigue Severity Scale (FSS) was assessed in an international population of 225 adults with Pompe disease, a metabolic disorder presenting as a slowly progressive proximal myopathy. The FSS scores were compared to those of healthy controls and the relationship between the level of fatigue and other patient characteristics was investigated.
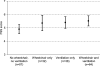
Results: The mean age of the participants was 47 (SD 13) years and the mean disease duration 11 (SD 8) years. 43% used a wheelchair and 46% had respiratory support, 29% needed both. 67% of the participants had a FSS score > or =5, indicating severe fatigue. The mean FSS score was 5.2 (SD 1.5), which was significantly higher than that of healthy controls (p < 0.001). Fatigue was not related to age, sex or disease duration. Patients who used a wheelchair or respiratory support were on average more fatigued than those who did not (p = 0.01). However, of the patients who did not use these aids, 59% also had a FSS score > or =5. FSS scores were highest among patients who reported a high frequency of sleep disorders, but patients who never experienced sleep difficulties were also fatigued (mean FSS score = 4.8).
Conclusion: Fatigue is highly prevalent among both mildly and severely affected adult patients with Pompe disease. The FSS appears a useful tool in assessing fatigue in Pompe disease.
Figures

Comment in
-
Adult onset Pompe disease associated with multiple sclerosis.J Neurol. 2011 Dec;258(12):2286-7. doi: 10.1007/s00415-011-6100-3. Epub 2011 May 26. J Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21614430 No abstract available.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1176/appi.ajp.160.2.350', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.160.2.350'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12562583', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12562583/'}]}
- Bardwell WA, Moore P, Ancoli-Israel S, Dimsdale JE (2003) Fatigue in obstructive sleep apnea: driven by depressive symptoms instead of apnea severity? Am J Psychiatry 160:350–355 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1023/A:1008916326411', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1008916326411'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10855341', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10855341/'}]}
- Buck D, Jacoby A, Baker GA, Ley H, Steen N (1999) Cross-cultural differences in health-related quality of life of people with epilepsy: findings from a European study. Qual Life Res 8:675–685 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15794-2', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(04)15794-2'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15043967', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15043967/'}]}
- Chaudhuri A, Behan PO (2004) Fatigue in neurological disorders. Lancet 363:978–988 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1177/0148607189013003321', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1177/0148607189013003321'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2503645', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2503645/'}]}
- Demey HE, Van Meerbeeck JP, Vandewoude MF, Prove AM, Martin JJ, Bossaert LL (1989) Respiratory insuf- ficiency in acid maltase deficiency: the effect of high protein diet. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 13:321–323 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1023/A:1008234310474', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1008234310474'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9496391', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9496391/'}]}
- Dimeo F, Stieglitz RD, Novelli-Fischer U, Fetscher S, Mertelsmann R, Keul J (1997) Correlation between physical performance and fatigue in cancer patients. Ann Oncol 8:1251–1255 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

