Comparative activities of daptomycin, linezolid, and tigecycline against catheter-related methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus bacteremic isolates embedded in biofilm
- PMID: 17353249
- PMCID: PMC1855569
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00350-06
Comparative activities of daptomycin, linezolid, and tigecycline against catheter-related methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus bacteremic isolates embedded in biofilm
Abstract
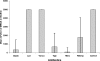
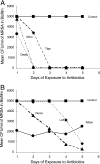
In the setting of catheter-related bloodstream infections, intraluminal antibiotic lock therapy could be useful for the salvage of vascular catheters. In this in vitro study, we investigated the efficacies of the newer antibiotics daptomycin, linezolid, and tigecycline, in comparison with those of vancomycin, minocycline, and rifampin, against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) embedded in biofilm. We also assessed the emergence of MRSA strains resistant to these antibiotics, alone or in combination with rifampin, after 4-hour daily use for catheter lock therapy. Minocycline, daptomycin, and tigecycline were more efficacious in inhibiting MRSA in biofilm than linezolid, vancomycin, and the negative control (P < 0.001) after the first day of exposure to these antibiotics, with minocycline being the most active, followed by daptomycin and then tigecycline, and with vancomycin and linezolid lacking activity, similar to the negative control. After 3 days of 4-hour daily exposures, daptomycin was the fastest in eradicating MRSA from biofilm, followed by minocycline and tigecycline, which were faster than linezolid, rifampin, and vancomycin (P < 0.001). When rifampin was used alone, it was the least effective in eradicating MRSA from biofilm after 5 days of 4-hour daily exposures, as it was associated with the emergence of rifampin-resistant MRSA. However, when rifampin was used in combination with other antibiotics, the combination was significantly effective in eliminating MRSA colonization in biofilm more rapidly than each of the antibiotics alone. In summary, daptomycin, minocycline, and tigecycline should be considered further for antibiotic lock therapy, and rifampin should be considered for enhanced antistaphylococcal activity but not as a single agent.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vitro activity of linezolid, tigecycline, and daptomycin on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus blood isolates from adult patients, 2006-2008: stratified analysis by vancomycin MIC.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2011 Oct;44(5):346-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2011.01.037. Epub 2011 Jan 20. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2011. PMID: 21524980
-
In vitro efficacy of antimicrobial agents against high-inoculum or biofilm-embedded meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with vancomycin minimal inhibitory concentrations equal to 2 μg/mL (VA2-MRSA).Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011 Jul;38(1):46-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.02.013. Epub 2011 May 6. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011. PMID: 21549575
-
Impact of Enterococcus faecalis on the bactericidal activities of arbekacin, daptomycin, linezolid, and tigecycline against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a mixed-pathogen pharmacodynamic model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Apr;50(4):1298-303. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.4.1298-1303.2006. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16569844 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: the superbug.Int J Infect Dis. 2010 Oct;14 Suppl 4:S7-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2010.05.003. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Int J Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20851011 Review.
-
Combating the growing problem of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: do the newer antibiotics represent a better alternative to vancomycin?Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2007 Jun;5(3):333-5. doi: 10.1586/14787210.5.3.333. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2007. PMID: 17547497 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Daptomycin use in patients with osteomyelitis: a preliminary report from the EU-CORE(SM) database.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013 Jul;68(7):1642-9. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt067. Epub 2013 Mar 20. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23515247 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of Tedizolid in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Experimental Foreign Body-Associated Osteomyelitis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Oct 21;60(11):6568-6572. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01248-16. Print 2016 Nov. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27550347 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilm-forming Staphylococcus epidermidis expressing vancomycin resistance early after adhesion to a metal surface.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:943056. doi: 10.1155/2015/943056. Epub 2015 Jan 31. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25802873 Free PMC article.
-
Bactericidal Effect of a Photoresponsive Carbon Monoxide-Releasing Nonwoven against Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Jun 20;60(7):4037-46. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00703-16. Print 2016 Jul. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27114272 Free PMC article.
-
Linezolid versus daptomycin treatment for periprosthetic joint infections: a retrospective cohort study.J Orthop Surg Res. 2019 Oct 24;14(1):334. doi: 10.1186/s13018-019-1375-7. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 31651331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey, E., N. Berry, and S. Cheesbrough. 2002. Antimicrobial lock therapy for catheter-related bacteraemia among patients on maintenance haemodialysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 58615-617. - PubMed
-
- Bleyer, A. J., L. Mason, G. Russell, I. I. Raad, and R. J. Sherertz. 2005. A randomized, controlled trial of a new vascular catheter flush solution (minocycline-EDTA) in temporary hemodialysis access. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 26520-524. - PubMed
-
- Chang, S., D. M. Sievert, J. C. Hageman, M. L. Boulton, F. C. Tenover, F. P. Downes, S. Shah, J. T. Rudrik, G. R. Pupp, W. J. Brown, D. Cardo, and S. K. Fridkin for the Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Investigative Team. 2003. Infection with vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus containing the vanA resistance gene. N. Engl. J. Med. 3481342-1347. - PubMed
-
- Chatzinikolaou, I., K. Finkel, H. Hanna, M. Boktour, J. Foringer, T. Ho, and I. Raad. 2003. Antibiotic-coated hemodialysis catheters for the prevention of vascular catheter-related infections: a prospective, randomized study. Am. J. Med. 115352-357. - PubMed
-
- Chatzinikolaou, I., T. F. Zipf, H. Hanna, J. Umphrey, W. M. Roberts, R. Sherertz, R. Hachem, and I. Raad. 2003. Minocycline-ethylenediamine-tetraacetate lock solution for the prevention of implantable port infections in children with cancer. Clin. Infect. Dis. 36116-119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

