Rivastigmine: a placebo controlled trial of twice daily and three times daily regimens in patients with Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 17353259
- PMCID: PMC2117538
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp.2006.099424
Rivastigmine: a placebo controlled trial of twice daily and three times daily regimens in patients with Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of rapidly titrated rivastigmine administered twice (BID) or three times (TID) daily in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Methods: This was a 26 week international, randomised, double blind, placebo controlled study in which 678 patients with probable AD received placebo or rivastigmine 2-12 mg/day BID or TID. Primary outcome measures included the cognitive subscale of the AD Assessment Scale (ADAS-cog) and categorical analysis of the Clinician Interview Based Impression of Change incorporating caregiver information (CIBIC-Plus). Secondary outcomes were the CIBIC-Plus change from baseline, Progressive Deterioration Scale, ADAS-cogA, Mini-Mental State Examination and Global Deterioration Scale.
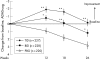
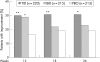
Results: At week 26, mean rivastigmine dose was 9.6 (2.76) mg/day in the TID group and 8.9 (2.93) mg/day in the BID group. Mean ADAS-cog changes from baseline in the TID and BID rivastigmine treated groups were -0.2 (SD 7.3) and 1.2 (SD 7.2) versus 2.8 (SD 7.2) for the placebo group (p<0.05). Differences between rivastigmine TID and placebo on the CIBIC-Plus categorical responder analysis were significant (31% vs 19%; p<0.05, intention to treat). No significant differences were seen between BID and placebo for this outcome measure. Adverse events were predominantly gastrointestinal, occurring mainly during dose titration. Withdrawal because of adverse events accounted for 17% of BID, 11% of TID and 9% of placebo patients.
Conclusions: Rivastigmine administered as a BID or TID regimen significantly benefited cognitive, function and global performances in AD patients. The TID regimen showed a tendency for superior tolerability and permitted titration to higher doses, an outcome that is significant as the efficacy of rivastigmine is dose related.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: HF has received honoraria for consulting, advisory boards and for participation in CME programs sponsored by Novartis. He has also received grant‐in‐aid funding for research from Novartis. RL is an employee of Novartis. The study was commissioned by Novartis Pharma AG in Switzerland.
Comment in
-
Rivastigmine three times daily improves cognition and response in Alzheimer's disease.Evid Based Ment Health. 2007 Nov;10(4):116. doi: 10.1136/ebmh.10.4.116. Evid Based Ment Health. 2007. PMID: 17962669 No abstract available.
References
-
- Davies P, Maloney A J. Selective loss of central cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 197621403 - PubMed
-
- Farlow M. A clinical overview of cholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer's disease. Int Psychogeriatr 200214(Suppl 1)93–126. - PubMed
-
- Brufani M, Filocamo L. Rational design of cholinesterase inhibitors. In: Giacobini E, ed. Cholinesterase and cholinesterase inhibitors. London: Martin Dunitz, 200027–46.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical