A comprehensive view of sex-specific issues related to cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 17353516
- PMCID: PMC1817670
- DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.051455
A comprehensive view of sex-specific issues related to cardiovascular disease
Erratum in
- CMAJ. 2007 Apr 24;176(9):1310
Abstract
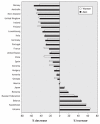
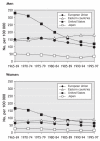
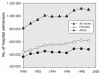
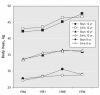
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of mortality in women. In fact, CVD is responsible for a third of all deaths of women worldwide and half of all deaths of women over 50 years of age in developing countries. The prevalence of CVD risk factor precursors is increasing in children. Retrospective analyses suggest that there are some clinically relevant differences between women and men in terms of prevalence, presentation, management and outcomes of the disease, but little is known about why CVD affects women and men differently. For instance, women with diabetes have a significantly higher CVD mortality rate than men with diabetes. Similarly, women with atrial fibrillation are at greater risk of stroke than men with atrial fibrillation. Historically, women have been underrepresented in clinical trials. The lack of good trial evidence concerning sex-specific outcomes has led to assumptions about CVD treatment in women, which in turn may have resulted in inadequate diagnoses and suboptimal management, greatly affecting outcomes. This knowledge gap may also explain why cardiovascular health in women is not improving as fast as that of men. Over the last decades, mortality rates in men have steadily declined, while those in women remained stable. It is also becoming increasingly evident that gender differences in cultural, behavioural, psychosocial and socioeconomic status are responsible, to various degrees, for the observed differences between women and men. However, the interaction between sex-and gender-related factors and CVD outcomes in women remains largely unknown.
Figures
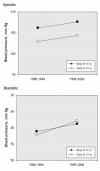
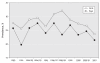
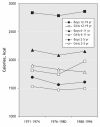
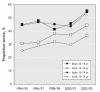

References
-
- The changing face of heart disease and stroke in Canada 2000. Ottawa: Heart and Stroke Foundation; 1999. Available: www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/ccdpc-cpcmc/cvdmcv/publications/pdf/card2ke.pdf (accessed 2000 Dec. 19).
-
- Thom T, Haase N, Rosamond W, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics — 2006 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 2005;113:e85-151. - PubMed
-
- Marrugat J, Elosua R, Aldasoro E, et al.; IBERICA Investigators. Regional variability in population acute myocardial infarction cumulative incidence and mortality rates in Spain 1997 and 1998. Eur J Epidemiol 2004;19:831-9. - PubMed
-
- Tunstall-Pedoe H, Kuulasmaa K, Mahonen M, et al. Contribution of trends in survival and coronary-event rates to changes in coronary heart disease mortality: 10-year results from 37 MONICA Project populations. Lancet 1999;353:1547-57. Available: www.heartstats.org/temp/TABsp2.2spweb04.xls (accessed 2006 Nov24). - PubMed
-
- Arciero TJ, Jacobsen SJ, Reeder GS, et al. Temporal trends in the incidence of coronary disease. Am J Med 2004;117:228-33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
