Serotonin transporter polymorphism, memory and hippocampal volume in the elderly: association and interaction with cortisol
- PMID: 17353910
- PMCID: PMC2084475
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001978
Serotonin transporter polymorphism, memory and hippocampal volume in the elderly: association and interaction with cortisol
Abstract
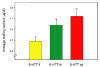
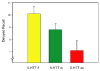
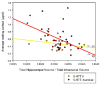
The s allele variant of the serotonin transporter gene (5-HTT) has recently been observed to moderate the relationship of stress to depression and anxiety. To date no study has considered interactive effects of 5-HTT genotype, stress and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) function on cognition in healthy, older adults, which may reflect developmental, functional or neurodegenerative effects of the serotonin transporter polymorphism. We investigated whether 5-HTT genotype interacts with cumulative life stress and HPA-axis measures of waking and diurnal cortisol slope to impact cognition in 154 non-depressed, older adults. Structural images of hippocampal volume were acquired on a subsample of 56 participants. The 5-HTT s allele was associated with both significantly lower delayed recall and higher waking cortisol levels. Presence of the s allele interacted with higher waking cortisol to negatively impact memory. We also observed a significant interaction of higher waking cortisol and the s allele on lower hippocampal volume. Smaller hippocampi and higher cortisol were associated with lower delayed recall only in s allele carriers. No impact or interactions of cumulative life stress with 5-HTT or cortisol were observed. This is the first investigation to identify an association of the 5-HTT s allele with poorer memory function in older adults. The interactive effects of the s allele and waking cortisol levels on reduced hippocampal volume and lower memory suggest that the negative effect of the serotonin polymorphism on memory is mediated by the HPA axis. Further, given the significant association of the s allele with higher waking cortisol in our investigation, future studies may be needed to evaluate the impact of the serotonin transporter polymorphism on any neuropsychiatric or behavioral outcome which is influenced by HPA axis function in older adults.
Figures

References
-
- Bondy B, Erfurth A, de Jonge S, Kruger M, Meyer H. Possible association of the short allele of the serotonin transporter promoter gene polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) with violent suicide. Mol Psychiatry. 2000;5:193–5. - PubMed
-
- Lesch KP, Bengel D, Heils A, Sabol SZ, Greenberg BD, Petri S, et al. Association of anxiety-related traits with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region. Science. 1996;274:1527–31. - PubMed
-
- Steffens DC, Svenson I, Marchuk DA, Levy RM, Hays JC, Flint EP, et al. Allelic differences in the serotonin transporter-linked polymorphic region in geriatric depression. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2002;10:185–91. - PubMed
-
- Heils A, Teufel A, Petri S, Stober G, Riederer P, Bengel D, et al. Allelic variation of human serotonin transporter gene expression. J Neurochem. 1996;66:2621–4. - PubMed
-
- Lesch KP, Gutknecht L. Pharmacogenetics of the serotonin transporter. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2005;29:1062–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

