Targeting homeostatic mechanisms of endoplasmic reticulum stress to increase susceptibility of cancer cells to fenretinide-induced apoptosis: the role of stress proteins ERdj5 and ERp57
- PMID: 17353921
- PMCID: PMC2360126
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603672
Targeting homeostatic mechanisms of endoplasmic reticulum stress to increase susceptibility of cancer cells to fenretinide-induced apoptosis: the role of stress proteins ERdj5 and ERp57
Abstract
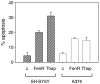
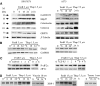
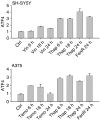
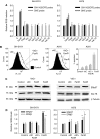
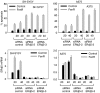
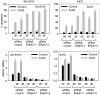
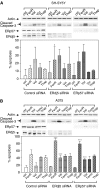
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) malfunction, leading to ER stress, can be a consequence of genome instability and hypoxic tissue environments. Cancer cells survive by acquiring or enhancing survival mechanisms to counter the effects of ER stress and these homeostatic responses may be new therapeutic targets. Understanding the links between ER stress and apoptosis may be approached using drugs specifically to target ER stress responses in cancer cells. The retinoid analogue fenretinide [N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide] is a new cancer preventive and chemotherapeutic drug, that induces apoptosis of some cancer cell types via oxidative stress, accompanied by induction of an ER stress-related transcription factor, GADD153. The aim of this study was to test the hypothesis that fenretinide induces ER stress in neuroectodermal tumour cells, and to elucidate the role of ER stress responses in fenretinide-induced apoptosis. The ER stress genes ERdj5, ERp57, GRP78, calreticulin and calnexin were induced in neuroectodermal tumour cells by fenretinide. In contrast to the apoptosis-inducing chemotherapeutic drugs vincristine and temozolomide, fenretinide induced the phosphorylation of eIF2alpha, expression of ATF4 and splicing of XBP-1 mRNA, events that define ER stress. In these respects, fenretinide displayed properties similar to the ER stress inducer thapsigargin. ER stress responses were inhibited by antioxidant treatment. Knockdown of ERp57 or ERdj5 by RNA interference in these cells increased the apoptotic response to fenretinide. These data suggest that downregulating homeostatic ER stress responses may enhance apoptosis induced by oxidative stress-inducing drugs acting through the ER stress pathway. Therefore, ER-resident proteins such as ERdj5 and ERp57 may represent novel chemotherapeutic targets.
Figures
References
-
- Albino AP, Juan G, Traganos F, Reinhart L, Connolly J, Rose DP, Darzynkiewicz Z (2000) Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of melanoma cells by docosahexaenoic acid: association with decreased pRb phosphorylation. Cancer Res 60: 4139–4145 - PubMed
-
- Bedard K, Szabo E, Michalak M, Opas M (2005) Cellular functions of endoplasmic reticulum chaperones calreticulin, calnexin, and ERp57. Int Rev Cytol 245: 91–121 - PubMed
-
- Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Hendershot LM, Harding HP, Ron D (2000) Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat Cell Biol 2: 326–332 - PubMed
-
- Brostrom CO, Brostrom MA (1998) Regulation of translational initiation during cellular responses to stress. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 58: 79–125 - PubMed
-
- Calfon M, Harding HP (2004) Marcie Calfon's & Heather Harding's protocol for detection of XBP-1 processing in mouse or human cells. http://saturn.med.nyu.edu/research/mp/ronlab/protocols/XBP-1.splicing.04...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

