Network-based prediction of protein function
- PMID: 17353930
- PMCID: PMC1847944
- DOI: 10.1038/msb4100129
Network-based prediction of protein function
Abstract
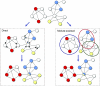
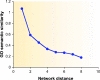
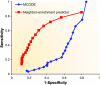
Functional annotation of proteins is a fundamental problem in the post-genomic era. The recent availability of protein interaction networks for many model species has spurred on the development of computational methods for interpreting such data in order to elucidate protein function. In this review, we describe the current computational approaches for the task, including direct methods, which propagate functional information through the network, and module-assisted methods, which infer functional modules within the network and use those for the annotation task. Although a broad variety of interesting approaches has been developed, further progress in the field will depend on systematic evaluation of the methods and their dissemination in the biological community.
Figures


References
-
- Adamcsek B, Palla G, Farkas IJ, Derenyi I, Vicsek T (2006) CFinder: locating cliques and overlapping modules in biological networks. Bioinformatics 22: 1021–1023 - PubMed
-
- Aebersold R, Mann M (2003) Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature 422: 198–207 - PubMed
-
- Arnau V, Mars S, Marin I (2005) Iterative cluster analysis of protein interaction data. Bioinformatics 21: 364–378 - PubMed
-
- Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet 25: 25–29 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

