Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor inhibits apoptotic neuron loss after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in rats
- PMID: 17359943
- PMCID: PMC1888563
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.01.144
Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor inhibits apoptotic neuron loss after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in rats
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of concern: "Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor inhibits apoptotic neuron loss after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in rats" [BRAIN RES, Volume 1145 (2007) 227-238].Brain Res. 2025 Aug 15;1861:149682. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2025.149682. Epub 2025 May 19. Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 40473331 No abstract available.
Abstract
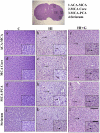
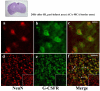
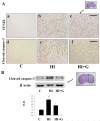
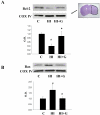
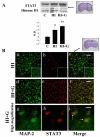
Neonatal hypoxia-ischemia (HI) is an important clinical problem with few effective treatments. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) is an endogenous peptide hormone of the hematopoietic system that has been shown to be neuroprotective in focal ischemia in vivo and is currently in phase I/II clinical trials for ischemic stroke in humans. We tested G-CSF in a rat model of neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in postnatal day 7 unsexed rat pups. Three groups of animals were used: hypoxia-ischemia (HI, n=67), hypoxia-ischemia with G-CSF treatment (HI+G, n=65), and healthy control (C, n=53). G-CSF (50 microg/kg, subcutaneous) was administered 1 h after HI and given on four subsequent days (five total injections). Animals were euthanized 24 h, 1, 2, and 3 weeks after HI. Assessment included brain weight, histology, immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting. G-CSF treatment was associated with improved quantitative brain weight and qualitative Nissl histology after hypoxia-ischemia. TUNEL demonstrated reduced apoptosis in group HI+G. Western blot demonstrated decreased expression of Bax and cleaved caspase-3 in group HI+G. G-CSF treatment was also associated with increased expression of STAT3, Bcl-2, and Pim-1, all of which may have participated in the anti-apoptotic effect of the drug. We conclude that G-CSF ameliorates hypoxic-ischemic brain injury and that this may occur in part by an inhibition of apoptotic cell death.
Figures


References
-
- Abe-Dohmae S, Harada N, Yamada K, Tanaka R. Bcl-2 gene is highly expressed during neurogenesis in the central nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;191:915–21. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar RS, Ness JM, Roth KA. Bcl-2 family regulation of neuronal development and neurodegeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1644:189–203. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann M, Moroy T. The serine/threonine kinase Pim-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37:726–730. - PubMed
-
- Calvert JW, Yin W, Patel M, Badr A, Mychaskiw G, Parent AD, Zhang JH. Hyperbaric oxygenation prevented brain injury induced by hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal rat model. Brain Res. 2002;951:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Ginis I, Hallenbeck JM. The protective effect of ceramide in immature rat brain hypoxia-ischemia involves up-regulation of bcl-2 and reduction of TUNEL-positive cells. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21:34–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

