Proteomic methods for analysis of S-nitrosation
- PMID: 17360249
- PMCID: PMC1997299
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.02.035
Proteomic methods for analysis of S-nitrosation
Abstract
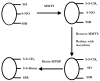
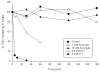
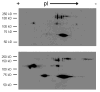
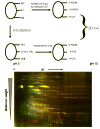
This review discusses proteomic methods to detect and identify S-nitrosated proteins. Protein S-nitrosation, the post-translational modification of thiol residues to form S-nitrosothiols, has been suggested to be a mechanism of cellular redox signaling by which nitric oxide can alter cellular function through modification of protein thiol residues. It has become apparent that methods that will detect and identify low levels of S-nitrosated protein in complex protein mixtures are required in order to fully appreciate the range, extent and selectivity of this modification in both physiological and pathological conditions. While many advances have been made in the detection of either total cellular S-nitrosation or individual S-nitrosothiols, proteomic methods for the detection of S-nitrosation are in relative infancy. This review will discuss the major methods that have been used for the proteomic analysis of protein S-nitrosation and discuss the pros and cons of this methodology.
Figures
References
-
- Stamler JS, Lamas S, Fang FC. Cell. 2001;106:675. - PubMed
-
- Hogg N, Singh RJ, Kalyanaraman B. FEBS Lett. 1996;382:223. - PubMed
-
- Folkes LK, Wardman P. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004;37:549. - PubMed
-
- DeMaster EG, Quast BJ, Redfern B, Nagasawa HT. Biochemistry. 1995;34:11494. - PubMed
-
- Pryor WA, Church DF, Govindan CK, Crank G. J Org Chem. 1982;47:159.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

