Strong effects of molecular topology on diffusion of entangled DNA molecules
- PMID: 17360350
- PMCID: PMC1820884
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0700137104
Strong effects of molecular topology on diffusion of entangled DNA molecules
Abstract
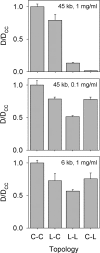
When long polymers such as DNA are in a highly concentrated state they may become entangled, leading to restricted self-diffusion. Here, we investigate the effect of molecular topology on diffusion in concentrated DNA solutions and find surprisingly large effects, even with molecules of modest length and concentration. We measured the diffusion coefficients of linear and relaxed circular molecules by tracking the Brownian motion of single molecules with fluorescence microscopy. Four possible cases were compared: linear molecules surrounded by linear molecules, circular molecules surrounded by linear molecules, linear molecules surrounded by circles, and circles surrounded by circles. In measurements with 45-kbp DNA at 1 mg/ml, we found that circles diffused approximately 100 times slower when surrounded by linear molecules than when surrounded by circles. In contrast, linear and circular molecules diffused at nearly the same rate when surrounded by circles, and circles diffused approximately 10 times slower than linears when surrounded by linears. Thus, diffusion in entangled DNA solutions strongly depends on topology of both the diffusing molecule and the surrounding molecules. This effect also strongly depends on DNA concentration and length. The differences largely disappeared when the concentration was lowered to 0.1 mg/ml or when the DNA length was lowered to 6 kb. Present theories cannot fully explain these effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Single-molecule measurements of trapped and migrating circular DNA during electrophoresis in agarose gels.Electrophoresis. 2006 Nov;27(22):4396-407. doi: 10.1002/elps.200600347. Electrophoresis. 2006. PMID: 17117465
-
Diffusion of isolated DNA molecules: dependence on length and topology.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 9;103(19):7310-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601903103. Epub 2006 Apr 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16648255 Free PMC article.
-
Marked difference in conformational fluctuation between giant DNA molecules in circular and linear forms.J Chem Phys. 2015 Apr 14;142(14):145101. doi: 10.1063/1.4916309. J Chem Phys. 2015. PMID: 25877594
-
Electrophoretic capture of circular DNA in gels.Electrophoresis. 2002 Aug;23(16):2549-61. doi: 10.1002/1522-2683(200208)23:16<2549::AID-ELPS2549>3.0.CO;2-Q. Electrophoresis. 2002. PMID: 12210158 Review.
-
Small DNA circles as probes of DNA topology.Biochem Soc Trans. 2013 Apr;41(2):565-70. doi: 10.1042/BST20120320. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013. PMID: 23514155 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of molecular architecture on ring polymer dynamics in semidilute linear polymer solutions.Nat Commun. 2019 Apr 15;10(1):1753. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09627-7. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30988290 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic systems for single DNA dynamics.Soft Matter. 2012 Jan 1;8(41):10560-10572. doi: 10.1039/C2SM26036K. Epub 2012 Jul 3. Soft Matter. 2012. PMID: 23139700 Free PMC article.
-
The entropic cost of polymer confinement.J Phys Chem B. 2012 Sep 6;116(35):10928-34. doi: 10.1021/jp302807r. Epub 2012 Aug 27. J Phys Chem B. 2012. PMID: 22905742 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Light Scattering Microrheology Reveals Multiscale Viscoelasticity of Polymer Gels and Precious Biological Materials.ACS Cent Sci. 2017 Dec 27;3(12):1294-1303. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.7b00449. Epub 2017 Dec 15. ACS Cent Sci. 2017. PMID: 29296670 Free PMC article.
-
Topological patterns in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of DNA knots.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Oct 6;112(40):E5471-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1506907112. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26351668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Gennes PG. Scaling Concepts in Polymer Physics. Ithaca, NY: Cornell Univ Press; 1979.
-
- Doi M, Edwards SF. The Theory of Polymer Dynamics. Oxford: Clarendon; 1986.
-
- McLeish TCB. Adv Phys. 2002;51:1379–1527.
-
- McLeish T. Science. 2002;297:2005–2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

