S-adenosylmethionine directly inhibits binding of 30S ribosomal subunits to the SMK box translational riboswitch RNA
- PMID: 17360376
- PMCID: PMC1829232
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0609956104
S-adenosylmethionine directly inhibits binding of 30S ribosomal subunits to the SMK box translational riboswitch RNA
Abstract
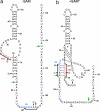
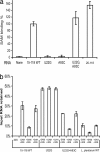
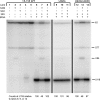
The S(MK) box is a conserved riboswitch motif found in the 5' untranslated region of metK genes [encoding S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) synthetase] in lactic acid bacteria, including Enterococcus, Streptococcus, and Lactococcus sp. Previous studies showed that this RNA element binds SAM in vitro, and SAM binding causes a structural rearrangement that sequesters the Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence by pairing with an anti-SD (ASD) element. A model was proposed in which SAM binding inhibits metK translation by preventing binding of the ribosome to the SD region of the mRNA. In the current work, the addition of SAM was shown to inhibit binding of 30S ribosomal subunits to S(MK) box RNA; in contrast, the addition of S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) had no effect. A mutant RNA, which has a disrupted SD-ASD pairing, was defective in SAM binding and showed no reduction of ribosome binding in the presence of SAM, whereas a compensatory mutation that restored SD-ASD pairing restored the response to SAM. Primer extension inhibition assays provided further evidence for SD-ASD pairing in the presence of SAM. These results strongly support the model that S(MK) box translational repression operates through occlusion of the ribosome binding site and that SAM binding requires the SD-ASD pairing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The SAM-responsive S(MK) box is a reversible riboswitch.Mol Microbiol. 2010 Dec;78(6):1393-402. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07410.x. Epub 2010 Oct 18. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21143313 Free PMC article.
-
The S(MK) box is a new SAM-binding RNA for translational regulation of SAM synthetase.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006 Mar;13(3):226-33. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1059. Epub 2006 Feb 19. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16491091
-
Crystal structures of the SAM-III/S(MK) riboswitch reveal the SAM-dependent translation inhibition mechanism.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008 Oct;15(10):1076-83. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1494. Epub 2008 Sep 21. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18806797 Free PMC article.
-
Riboswitches that sense S-adenosylmethionine and S-adenosylhomocysteine.Biochem Cell Biol. 2008 Apr;86(2):157-68. doi: 10.1139/O08-008. Biochem Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18443629 Review.
-
Recognition of S-adenosylmethionine by riboswitches.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Mar-Apr;2(2):299-311. doi: 10.1002/wrna.63. Epub 2011 Jan 12. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21957011 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phylogenetic analysis and comparative genomics of purine riboswitch distribution in prokaryotes.Evol Bioinform Online. 2012;8:589-609. doi: 10.4137/EBO.S10048. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Evol Bioinform Online. 2012. PMID: 23170063 Free PMC article.
-
Variable sequences outside the SAM-binding core critically influence the conformational dynamics of the SAM-III/SMK box riboswitch.J Mol Biol. 2011 Jun 24;409(5):786-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.04.039. Epub 2011 Apr 27. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21549712 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering ligand-responsive gene-control elements: lessons learned from natural riboswitches.Gene Ther. 2009 Oct;16(10):1189-201. doi: 10.1038/gt.2009.81. Epub 2009 Jul 9. Gene Ther. 2009. PMID: 19587710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional and translational S-box riboswitches differ in ligand-binding properties.J Biol Chem. 2020 May 15;295(20):6849-6860. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.012853. Epub 2020 Mar 24. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32209653 Free PMC article.
-
The SAM-responsive S(MK) box is a reversible riboswitch.Mol Microbiol. 2010 Dec;78(6):1393-402. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07410.x. Epub 2010 Oct 18. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21143313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grundy FJ, Henkin TM. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2004;7:126–131. - PubMed
-
- Vitreschak AG, Rodionov DA, Mironov AA, Gelfand MS. Trends Genet. 2004;20:44–50. - PubMed
-
- Nudler E, Mironov AS. Trends Biochem. 2004;29:11–17. - PubMed
-
- Winkler WC, Breaker RR. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2005;59:487–517. - PubMed
-
- Grundy FJ, Henkin TM. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2006;41:329–338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

