Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha stabilization by carbon monoxide results in cytoprotective preconditioning
- PMID: 17360382
- PMCID: PMC1820823
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0609611104
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha stabilization by carbon monoxide results in cytoprotective preconditioning
Abstract
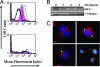
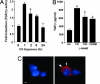
The most salient feature of carbon monoxide (CO)-mediated cytoprotection is the suppression of inflammation and cell death. One of the important cellular targets of CO is the macrophage (mphi). Many studies have shown that exposure of mphi to CO results in the generation of an antiinflammatory phenotype; however, these reports have ignored the effect of CO alone on the cell before stimulation. Most investigations have focused on the actions of CO in modulating the response to noxious stimuli. We demonstrate here that exposure of mphi to CO results in a significant and transient burst of reactive oxygen species (ROS) arising from the mitochondria (mitochondria-deficient mphi do not respond to CO to produce ROS). The ROS promote rapid activation and stabilization of the transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha), which regulates expression of genes involved in inflammation, metabolism, and cell survival. The increase in HIF-1alpha expression induced by CO results in regulated expression of TGF-beta, a potent antiinflammatory cytokine. CO-induced HIF-1alpha and TGF-beta expression are necessary to prevent anoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in mphi. Furthermore, blockade of HIF-1alpha using RNA interference and HIF-1alpha-cre-lox mphi resulted in a loss of TGF-beta expression and CO-induced protection. A similar mechanism of CO-induced protection was operational in vivo to protect against lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. Taken together, we conclude that CO conditions the mphi via a HIF-1alpha and TGF-beta-dependent mechanism and we elucidate the earliest events in mphi signaling that lead to and preserve cellular homeostasis at the site of injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: L.E.O. is a paid consultant of Linde Healthcare.
Figures


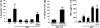

References
-
- Mazzola S, Forni M, Albertini M, Bacci ML, Zannoni A, Gentilini F, Lavitrano M, Bach FH, Otterbein LE, Clement MG. FASEB J. 2005;14:2045–2047. - PubMed
-
- Moore BA, Overhaus M, Whitcomb J, Ifedigbo E, Choi AM, Otterbein LE, Bauer AJ. Crit Care Med. 2005;6:1317–1326. - PubMed
-
- Neto JS, Nakao A, Kimizuka K, Romanosky AJ, Stolz DB, Uchiyama T, Nalesnik MA, Otterbein LE, Murase N. Am J Physiol. 2004;287:F979–F989. - PubMed
-
- Ameredes BT, Otterbein LE, Kohut LK, Gligonic AL, Calhoun WJ, Choi AM. Am J Physiol. 2003;285:L1270–L1276. - PubMed
-
- Zuckerbraun BS, Otterbein LE, Boyle P, Jaffe R, Upperman J, Zamora R, Ford HR. Am J Physiol. 2005;289:G607–G613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

