Direct visualization of Escherichia coli chemotaxis receptor arrays using cryo-electron microscopy
- PMID: 17360429
- PMCID: PMC1820660
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0610106104
Direct visualization of Escherichia coli chemotaxis receptor arrays using cryo-electron microscopy
Abstract
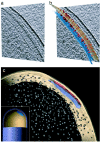
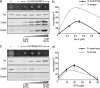
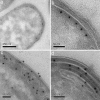
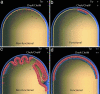
Signal transduction in bacterial chemotaxis is initiated by the binding of extracellular ligands to a specialized family of methyl-accepting chemoreceptor proteins. Chemoreceptors cluster at distinct regions of the cell and form stable ternary complexes with the histidine autokinase CheA and the adapter protein CheW. Here we report the direct visualization and spatial organization of chemoreceptor arrays in intact Escherichia coli cells by using cryo-electron tomography and biochemical techniques. In wild-type cells, ternary complexes are arranged as an extended lattice, which may or may not be ordered, with significant variations in the size and specific location among cells in the same population. In the absence of CheA and CheW, chemoreceptors do not form observable clusters and are diffusely localized to the cell pole. At disproportionately high receptor levels, membrane invaginations containing nonfunctional, axially interacting receptor assemblies are formed. However, functional chemoreceptor arrays can be reestablished by increasing cellular levels of CheA and CheW. Our results demonstrate that chemotaxis in E. coli requires the presence of chemoreceptor arrays and that the formation of these arrays requires the scaffolding interactions of the signaling molecules CheA and CheW.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CheW binding interactions with CheA and Tar. Importance for chemotaxis signaling in Escherichia coli.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 21;277(25):22251-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110908200. Epub 2002 Mar 28. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11923283
-
Core unit of chemotaxis signaling complexes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jun 7;108(23):9390-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1104824108. Epub 2011 May 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21606342 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral density of receptor arrays in the membrane plane influences sensitivity of the E. coli chemotaxis response.EMBO J. 2011 May 4;30(9):1719-29. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.77. Epub 2011 Mar 25. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21441899 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulus response coupling in bacterial chemotaxis: receptor dimers in signalling arrays.Mol Microbiol. 1998 Nov;30(3):459-66. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.01066.x. Mol Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9822812 Review.
-
Bacterial chemotaxis coupling protein: Structure, function and diversity.Microbiol Res. 2019 Feb;219:40-48. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2018.11.001. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Microbiol Res. 2019. PMID: 30642465 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural insights into the assembly of large oligomeric signalosomes in the Toll-like receptor-interleukin-1 receptor superfamily.Sci Signal. 2012 May 29;5(226):re3. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2003124. Sci Signal. 2012. PMID: 22649099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of the recA gene decreases oral but not intraperitoneal fitness of Salmonella enterica.Infect Immun. 2010 Jul;78(7):3217-25. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01321-09. Epub 2010 May 10. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20457791 Free PMC article.
-
Biological imaging with 4D ultrafast electron microscopy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 1;107(22):9933-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005653107. Epub 2010 May 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20479261 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular localization of predicted transmembrane and soluble chemoreceptors in Sinorhizobium meliloti.J Bacteriol. 2009 Sep;191(18):5724-33. doi: 10.1128/JB.01286-08. Epub 2009 Jul 17. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19617359 Free PMC article.
-
Locating macromolecules and determining structures inside bacterial cells using electron cryotomography.Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2018 Sep;1866(9):973-981. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2018.06.003. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2018. PMID: 29908328 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parkinson JS, Ames P, Studdert CA. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005;8:116–121. - PubMed
-
- Sourjik V. Trends Microbiol. 2004;12:569–576. - PubMed
-
- Wadhams GH, Armitage JP. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:1024–1037. - PubMed
-
- Maddock JR, Shapiro L. Science. 1993;259:1717–1723. - PubMed
-
- Sourjik V, Berg HC. Mol Microbiol. 2000;37:740–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

