CD8 tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are predictive of survival in muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma
- PMID: 17360461
- PMCID: PMC1820692
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0611618104
CD8 tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are predictive of survival in muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma
Abstract
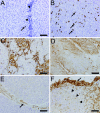
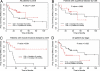
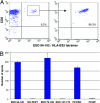
Tumor-infiltrating cytotoxic T lymphocytes (TILs), including CD8 TILs, have been associated with favorable clinical outcomes in multiple tumor types. Tumor-infiltrating CD8 T cells and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I expression in urothelial carcinoma (UC) have not been previously reported. Most immune responses are mediated by local cytotoxic lymphocytes (CD8 T cells), which can eradicate tumor cells by recognizing tumor-associated antigens presented by MHC class I molecules. Here we analyzed the presence of intratumoral CD8 T cells, the expression of MHC class I antigen, and the expression of the NY-ESO-1 tumor antigen in UC samples and correlated our findings with clinical outcome. Immunohistochemical staining for intratumoral CD8 T cells in tissue samples from 69 patients with UC showed that patients with advanced UC (pT2, pT3, or pT4) and higher numbers of CD8 TILs within the tumor (> or =8) had better disease-free survival (P < 0.001) and overall survival (P = 0.018) than did patients with similar-staged UC and fewer intratumoral CD8 TILs. We conclude that the extent of intratumoral CD8 TILs is an important prognostic indicator in advanced UC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alexandroff AB, Jackson AM, O'Donnell MA, James K. Lancet. 1999;353:1689–1694. - PubMed
-
- Ponticello A, Perna F, Maione S, Stradolini M, Testa G, Terrazzano G, Ruggerio G, Malerba M, Sanduzzi A. Respir Med. 2004;98:509–514. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Conejo-Garcia JR, Katsaros D, Gimott PA, Massobrio M, Regnani G, Makrigiannakis A, Gray H, Schlienger K, Liebman MN, et al. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:203–213. - PubMed
-
- Schumacher K, Haensch W, Roefzaad C, Schlag PM. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3932–3936. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

