WNK4 regulates activity of the epithelial Na+ channel in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 17360470
- PMCID: PMC1805455
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0611727104
WNK4 regulates activity of the epithelial Na+ channel in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
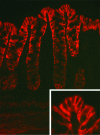
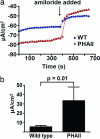
Homeostasis of intravascular volume, Na(+), Cl(-), and K(+) is interdependent and determined by the coordinated activities of structurally diverse mediators in the distal nephron and the distal colon. The behavior of these flux pathways is regulated by the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; however, the mechanisms that allow independent modulation of individual elements have been obscure. Previous work has shown that mutations in WNK4 cause pseudohypoaldosteronism type II (PHAII), a disease featuring hypertension with hyperkalemia, due to altered activity of specific Na-Cl cotransporters, K(+) channels, and paracellular Cl(-) flux mediators of the distal nephron. By coexpression studies in Xenopus oocytes, we now demonstrate that WNK4 also inhibits the epithelial Na(+) channel (ENaC), the major mediator of aldosterone-sensitive Na(+) (re)absorption, via a mechanism that is independent of WNK4's kinase activity. This inhibition requires intact C termini in ENaC beta- and gamma-subunits, which contain PY motifs used to target ENaC for clearance from the plasma membrane. Importantly, PHAII-causing mutations eliminate WNK4's inhibition of ENaC, thereby paralleling other effects of PHAII to increase sodium balance. The relevance of these findings in vivo was studied in mice harboring PHAII-mutant WNK4. The colonic epithelium of these mice demonstrates markedly increased amiloride-sensitive Na(+) flux compared with wild-type littermates. These studies identify ENaC as a previously unrecognized downstream target of WNK4 and demonstrate a functional role for WNK4 in the regulation of colonic Na(+) absorption. These findings support a key role for WNK4 in coordinating the activities of diverse flux pathways to achieve integrated fluid and electrolyte homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

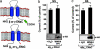
Similar articles
-
An SGK1 site in WNK4 regulates Na+ channel and K+ channel activity and has implications for aldosterone signaling and K+ homeostasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Mar 6;104(10):4025-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611728104. Epub 2007 Feb 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17360471 Free PMC article.
-
WNK3, a kinase related to genes mutated in hereditary hypertension with hyperkalaemia, regulates the K+ channel ROMK1 (Kir1.1).J Physiol. 2006 Mar 1;571(Pt 2):275-86. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.102202. Epub 2005 Dec 15. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16357011 Free PMC article.
-
WNK4 regulates apical and basolateral Cl- flux in extrarenal epithelia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Feb 17;101(7):2064-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308434100. Epub 2004 Feb 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14769928 Free PMC article.
-
[WNK1 and WNK4, new players in salt and water homeostasis].Med Sci (Paris). 2005 Jan;21(1):55-60. doi: 10.1051/medsci/200521155. Med Sci (Paris). 2005. PMID: 15639021 Review. French.
-
Life and death of the distal nephron: WNK4 and NCC as major players.Cell Metab. 2006 Nov;4(5):335-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.10.007. Cell Metab. 2006. PMID: 17084706 Review.
Cited by
-
Decreased ENaC expression compensates the increased NCC activity following inactivation of the kidney-specific isoform of WNK1 and prevents hypertension.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Oct 19;107(42):18109-14. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1006128107. Epub 2010 Oct 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20921400 Free PMC article.
-
Immunolocalization of WNK4 in mouse kidney.Histochem Cell Biol. 2011 Jul;136(1):25-35. doi: 10.1007/s00418-011-0827-x. Epub 2011 Jun 10. Histochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21660484
-
An unexpected journey: conceptual evolution of mechanoregulated potassium transport in the distal nephron.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Feb 15;310(4):C243-59. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00328.2015. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26632600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Association of WNK4 Gene, Ala589Ser Polymorphism in Essential Hypertension, and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Malaysia.J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:8219543. doi: 10.1155/2016/8219543. Epub 2016 May 29. J Diabetes Res. 2016. PMID: 27314050 Free PMC article.
-
A patient with pseudohypoaldosteronism type II caused by a novel mutation in WNK4 gene.Endocrine. 2008 Jun;33(3):230-4. doi: 10.1007/s12020-008-9084-8. Endocrine. 2008. PMID: 19016006
References
-
- Schultheis PJ, Clarke LL, Meneton P, Miller ML, Soleimani M, Gawenis LR, Riddle TM, Duffy JJ, Doetschman T, Wang T, et al. Nat Genet. 1998;19:282–285. - PubMed
-
- Kunzelmann K, Mall M. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:245–289. - PubMed
-
- Lifton RP, Gharavi AG, Geller DS. Cell. 2001;104:545–556. - PubMed
-
- Pearce D. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2001;12:341–347. - PubMed
-
- Kamynina E, Debonneville C, Bens M, Vandewalle A, Staub O. FASEB J. 2001;15:204–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

