A phase I clinical trial with monoclonal antibody ch806 targeting transitional state and mutant epidermal growth factor receptors
- PMID: 17360479
- PMCID: PMC1805701
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0611693104
A phase I clinical trial with monoclonal antibody ch806 targeting transitional state and mutant epidermal growth factor receptors
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Oct 2;104(40):15965. Ritter, Gerd [added]
Abstract
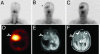
An array of cell-surface antigens expressed by human cancers have been identified as targets for antibody-based therapies. The great majority of these antibodies do not have specificity for cancer but recognize antigens expressed on a range of normal cell types (differentiation antigens). Over the past two decades, our group has analyzed thousands of mouse monoclonal antibodies for cancer specificity and identified a battery of antibodies with limited representation on normal human cells. The most tumor-specific of these antibodies is 806, an antibody that detects a unique epitope on the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) that is exposed only on overexpressed, mutant, or ligand-activated forms of the receptor in cancer. In vitro immunohistochemical specificity analysis shows little or no detectable 806 reactivity with normal tissues, even those with high levels of wild-type (wt)EGFR expression. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that 806 specifically targets a subset of EGFR expressed on tumor cells, and has significant anti-tumor effects on human tumor xenografts, primarily through abrogation of signaling pathways. The present clinical study was designed to examine the in vivo specificity of a chimeric form of mAb 806 (ch806) in a tumor targeting/biodistribution/pharmacokinetic analysis in patients with diverse tumor types. ch806 showed excellent targeting of tumor sites in all patients, no evidence of normal tissue uptake, and no significant toxicity. These in vitro and in vivo characteristics of ch806 distinguish it from all other antibodies targeting EGFR.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: A.M.S., A.A.J., A.W.B., T.G.J., and L.J.O. are coinventors of a patent for monoclonal antibody 806. A.M.S. and F.E.S. are consultants to Life Sciences Pharmaceuticals, which has the license for ch806. L.J.O. is a noncompensated board member of Life Sciences Pharmaceuticals.
Figures


References
-
- Rettig WJ, Old LJ. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:481–511. - PubMed
-
- Van den Eynde BJ, Scott AM. In: Encylopedia of Immunology. Roitt DPJ, Roitt IM, editors. London: Academic; 1998. pp. 2424–2431.
-
- Maloney DG, Grillo-Lopez AJ, White CA, Bodkin D, Schilder RJ, Neidhart JA, Janakiraman N, Foon KA, Liles TM, Dallaire BK, et al. Blood. 1997;90:2188–2195. - PubMed
-
- Baselga J, Artega CL. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2445–2449. - PubMed
-
- Voldborg BR, Damstrup L, Spang-Thomsen M, Poulsen HS. Ann Oncol. 1997;8:1197–1206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

