Adenosine regulation of alveolar fluid clearance
- PMID: 17360481
- PMCID: PMC1820712
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0601117104
Adenosine regulation of alveolar fluid clearance
Abstract
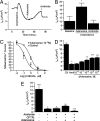
Adenosine is a purine nucleoside that regulates cell function through G protein-coupled receptors that activate or inhibit adenylyl cyclase. Based on the understanding that cAMP regulates alveolar epithelial active Na(+) transport, we hypothesized that adenosine and its receptors have the potential to regulate alveolar ion transport and airspace fluid content. Herein, we report that type 1 (A(1)R), 2a (A(2a)R), 2b (A(2b)R), and 3 (A(3)R) adenosine receptors are present in rat and mouse lungs and alveolar type 1 and 2 epithelial cells (AT1 and AT2). Rat AT2 cells generated and produced cAMP in response to adenosine, and micromolar concentrations of adenosine were measured in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from mice. Ussing chamber studies of rat AT2 cells indicated that adenosine affects ion transport through engagement of A(1)R, A(2a)R, and/or A(3)R through a mechanism that increases CFTR and amiloride-sensitive channel function. Intratracheal instillation of low concentrations of adenosine (< or =10(-8)M) or either A(2a)R- or A(3)R-specific agonists increased alveolar fluid clearance (AFC), whereas physiologic concentrations of adenosine (> or =10(-6)M) reduced AFC in mice and rats via an A(1)R-dependent pathway. Instillation of a CFTR inhibitor (CFTR(inh-172)) attenuated adenosine-mediated down-regulation of AFC, suggesting that adenosine causes Cl(-) efflux by means of CFTR. These studies report a role for adenosine in regulation of alveolar ion transport and fluid clearance. These findings suggest that physiologic concentrations of adenosine allow the alveolar epithelium to counterbalance active Na(+) absorption with Cl(-) efflux through engagement of the A(1)R and raise the possibility that adenosine receptor ligands can be used to treat pulmonary edema.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

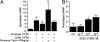
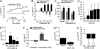
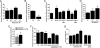
References
-
- Ware LB, Matthay MA. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:1376–1383. - PubMed
-
- Olivera W, Ridge K, Sznajder J. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;152:1229–1234. - PubMed
-
- Saldias FJ, Azzam ZS, Ridge KM, Yeldandi A, Rutschman DH, Schraufnagel D, Sznajder JI. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001;281:L591–L597. - PubMed
-
- Modelska K, Matthay M, Brown L, Deutch E, Lu L, Pittet J. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 1999;276:L844–L857. - PubMed
-
- Chunn JL, Young HW, Banerjee SK, Colasurdo GN, Blackburn MR. J Immunol. 2001;167:4676–4685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL 31197/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL051173/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL031197/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 72871/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 51173/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL079094/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 71042/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 66211/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES015024/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL066211/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 79094/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL031197/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL072871/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ES 015024/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071042/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

