Selective gene silencing in activated leukocytes by targeting siRNAs to the integrin lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1
- PMID: 17360483
- PMCID: PMC1820714
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0608491104
Selective gene silencing in activated leukocytes by targeting siRNAs to the integrin lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1
Abstract
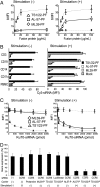
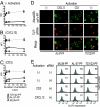
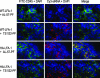
Silencing gene expression by RNAi is a powerful method for exploring gene function and validating drug targets and potentially for therapy. Lymphocytes and other primary blood cells are resistant to lipid-based transfection in vitro and are difficult to target in vivo. We show here that antibody-protamine fusion proteins targeting the human integrin lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) efficiently deliver siRNAs and specifically induce silencing in primary lymphocytes, monocytes, and dendritic cells. Moreover, a fusion protein constructed from an antibody that preferentially recognizes activation-dependent conformational changes in LFA-1 selectively targets activated leukocytes and can be used to suppress gene expression and cell proliferation only in activated lymphocytes. The siRNA-fusion protein complexes do not cause lymphocyte activation or induce IFN responses. K562 cells expressing latent WT or constitutively activated LFA-1 engrafted in the lungs of SCID mice are selectively targeted by intravenously injected fusion protein-siRNA complexes, demonstrating the potential in vivo applicability of LFA-1-directed siRNA delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
Author contributions: D.P. and P.Z. contributed equally to this work; D.P., P.Z., C.V.C., J.L., and M.S. designed research; D.P., P.Z., and C.V.C. performed research; C.V.C., J.L., and M.S. contributed new reagents/analytic tools; D.P., P.Z., C.V.C., J.L., and M.S. analyzed data; and D.P., J.L., and M.S. wrote the paper. D.P., P.Z., C.V.C., and M.S. declare no conflict of interest. J.L. declares a financial interest. A prorizional patent on the antibody fusion protein method for siRNA delivery has been licensed.
Figures

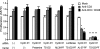
References
-
- Dykxhoorn DM, Lieberman J. Annu Rev Med. 2005;56:401–423. - PubMed
-
- Goffinet C, Keppler OT. FASEB J. 2006;20:500–502. - PubMed
-
- Marodon G, Mouly E, Blair EJ, Frisen C, Lemoine FM, Klatzmann D. Blood. 2003;101:3416–3423. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Lu H, LiWang P, Sili U, Templeton NS. Mol Ther. 2003;8:629–636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

