Ischemic insults promote epigenetic reprogramming of mu opioid receptor expression in hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 17360495
- PMCID: PMC1820727
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0611704104
Ischemic insults promote epigenetic reprogramming of mu opioid receptor expression in hippocampal neurons
Abstract
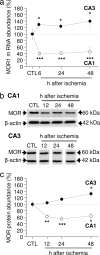
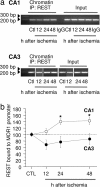
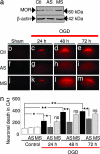
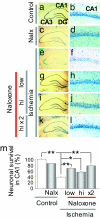
Transient global ischemia is a neuronal insult that induces delayed, selective death of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. A mechanism underlying ischemia-induced cell death is activation of the gene silencing transcription factor REST (repressor element-1 silencing transcription factor)/NRSF (neuron-restrictive silencing factor) and REST-dependent suppression of the AMPA receptor subunit GluR2 in CA1 neurons destined to die. Here we show that REST regulates an additional gene target, OPRM1 (mu opioid receptor 1 or MOR-1). MORs are abundantly expressed by basket cells and other inhibitory interneurons of CA1. Global ischemia induces a marked decrease in MOR-1 mRNA and protein expression that is specific to the selectively vulnerable area CA1, as assessed by quantitative real-time RT-PCR, Western blotting, and ChIP. We further show that OPRM1 gene silencing is REST-dependent and occurs via epigenetic modifications. Ischemia promotes deacetylation of core histone proteins H3 and H4 and dimethylation of histone H3 at lysine-9 (H3-K9) over the MOR-1 promoter, an signature of epigenetic gene silencing. Acute knockdown of MOR-1 gene expression by administration of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to hippocampal slices in vitro or injection of the MOR antagonist naloxone to rats in vivo affords protection against ischemia-induced death of CA1 pyramidal neurons. These findings implicate MORs in ischemia-induced death of CA1 pyramidal neurons and document epigenetic remodeling of expression of OPRM1 in CA1 inhibitory interneurons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

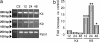
Similar articles
-
The gene silencing transcription factor REST represses miR-132 expression in hippocampal neurons destined to die.J Mol Biol. 2014 Oct 9;426(20):3454-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.07.032. Epub 2014 Aug 6. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25108103 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemic insults derepress the gene silencer REST in neurons destined to die.J Neurosci. 2003 Mar 15;23(6):2112-21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-06-02112.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12657670 Free PMC article.
-
Remodeling of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid receptor subunit composition in hippocampal neurons after global ischemia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Nov 21;97(24):13360-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.24.13360. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11087875 Free PMC article.
-
Interneurons in rat hippocampus after cerebral ischemia. Morphometric, functional, and therapeutic investigations.Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1993;150:1-32. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1993. PMID: 7907456 Review.
-
Signaling mechanisms of μ-opioid receptor (MOR) in the hippocampus: disinhibition versus astrocytic glutamate regulation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jan;78(2):415-426. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03595-8. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 32671427 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of histone deacetylase by butyrate protects rat liver from ischemic reperfusion injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Nov 14;15(11):21069-79. doi: 10.3390/ijms151121069. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25405737 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of Epigenetics in Cerebral Ischemia.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Apr;54(3):1887-1905. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9788-3. Epub 2016 Feb 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26894397 Review.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibition reduces myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice.FASEB J. 2008 Oct;22(10):3549-60. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-108548. Epub 2008 Jul 7. FASEB J. 2008. PMID: 18606865 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Re-Expression of Repressor Element 1-Silencing Transcription Factor Contributes to Cardiac Vagal Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 May 14;14(5):588. doi: 10.3390/antiox14050588. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427470 Free PMC article.
-
Sp3/REST/HDAC1/HDAC2 Complex Represses and Sp1/HIF-1/p300 Complex Activates ncx1 Gene Transcription, in Brain Ischemia and in Ischemic Brain Preconditioning, by Epigenetic Mechanism.J Neurosci. 2015 May 13;35(19):7332-48. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2174-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25972164 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

