Needle-free delivery of macromolecules across the skin by nanoliter-volume pulsed microjets
- PMID: 17360511
- PMCID: PMC1838589
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0700182104
Needle-free delivery of macromolecules across the skin by nanoliter-volume pulsed microjets
Abstract
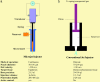
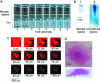
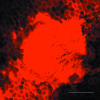
Needle-free liquid jet injectors were invented >50 years ago for the delivery of proteins and vaccines. Despite their long history, needle-free liquid jet injectors are not commonly used as a result of frequent pain and bruising. We hypothesized that pain and bruising originate from the deep penetration of the jets and can potentially be addressed by minimizing the penetration depth of jets into the skin. However, current jet injectors are not designed to maintain shallow dermal penetration depths. Using a new strategy of jet injection, pulsed microjets, we report on delivery of protein drugs into the skin without deep penetration. The high velocity (v >100 m/s) of microjets allows their entry into the skin, whereas the small jet diameters (50-100 mum) and extremely small volumes (2-15 nanoliters) limit the penetration depth ( approximately 200 mum). In vitro experiments confirmed quantitative delivery of molecules into human skin and in vivo experiments with rats confirmed the ability of pulsed microjets to deliver therapeutic doses of insulin across the skin. Pulsed microjet injectors could be used to deliver drugs for local as well as systemic applications without using needles.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: I.H., J.B., R.R., and R.S. are employees and/or stockholders of StrataGent Life Sciences. S.M. and D.A.F. are scientific advisors and stockholders.
Figures

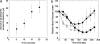
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

