Galphai2-mediated signaling events in the endothelium are involved in controlling leukocyte extravasation
- PMID: 17360531
- PMCID: PMC1838609
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0700185104
Galphai2-mediated signaling events in the endothelium are involved in controlling leukocyte extravasation
Abstract
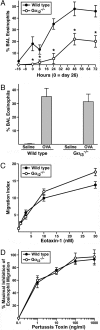
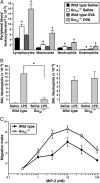
The trafficking of leukocytes from the blood to sites of inflammation is the cumulative result of receptor-ligand-mediated signaling events associated with the leukocytes themselves as well as with the underlying vascular endothelium. Our data show that Galpha(i) signaling pathways in the vascular endothelium regulate a critical step required for leukocyte diapedesis. In vivo studies using knockout mice demonstrated that a signaling event in a non-lymphohematopoietic compartment of the lung prevented the recruitment of proinflammatory leukocytes. Intravital microscopy showed that blockade was at the capillary endothelial surface and ex vivo studies of leukocyte trafficking demonstrated that a Galpha(i)-signaling event in endothelial cells was required for transmigration. Collectively, these data suggest that specific Galpha(i2)-mediated signaling between endothelial cells and leukocytes is required for the extravasation of leukocytes and for tissue-specific accumulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Worthylake RA, Burridge K. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13:569–577. - PubMed
-
- Jiang M, Spicher K, Boulay G, Martin-Requero A, Dye CA, Rudolph U, Birnbaumer L. Methods Enzymol. 2002;344:277–298. - PubMed
-
- Wise A, Gearing K, Rees S. Drug Discov Today. 2002;7:235–246. - PubMed
-
- Wettschureck N, Offermanns S. Physiol Rev. 2005;85:1159–1204. - PubMed
-
- Wilkie TM, Gilbert DJ, Olsen AS, Chen X-N, Amatruda TT, Korenberg JR, Trask BJ, de Jong P, Reed RR, Simon MI, et al. Nat Genet. 1992;1:85–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL068171/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK 19318/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R29 AI035796/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL 065228/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL079304/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 079304/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K26 RR019709/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL069428/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI035796/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 35796/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL058723/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HL058723/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM034236/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065228/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 058723/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 68171/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K26 RR 019709/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- GM 34236/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

