Triptolide is a traditional Chinese medicine-derived inhibitor of polycystic kidney disease
- PMID: 17360534
- PMCID: PMC1838612
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0700499104
Triptolide is a traditional Chinese medicine-derived inhibitor of polycystic kidney disease
Abstract
During kidney organogenesis, tubular epithelial cells proliferate until a functional tubule is formed as sensed by cilia bending in response to fluid flow. This flow-induced ciliary mechanosensation opens the calcium (Ca(2+)) channel polycystin-2 (PC2), resulting in a calcium flux-mediated cell cycle arrest. Loss or mutation of either PC2 or its regulatory protein polycystin-1 (PC1) results in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), characterized by cyst formation and growth and often leading to renal failure and death. Here we show that triptolide, the active diterpene in the traditional Chinese medicine Lei Gong Teng, induces Ca(2+) release by a PC2-dependent mechanism. Furthermore, in a murine model of ADPKD, triptolide arrests cellular proliferation and attenuates overall cyst formation by restoring Ca(2+) signaling in these cells. We anticipate that small molecule induction of PC2-dependent calcium release is likely to be a valid therapeutic strategy for ADPKD.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: C.M.C. and S.S. are currently exploring the commercial implications of these findings and declare a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

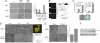
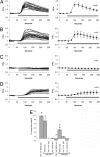
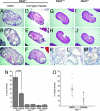
References
-
- Gabow PA, Grantham JJ. Polycystic Kidney Disease. Boston: Little, Brown; 1997.
-
- Koulen P, Cai Y, Geng L, Maeda Y, Nishimura S, Witzgall R, Ehrlich BE, Somlo S. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:191–197. - PubMed
-
- Anyatonwu GI, Ehrlich BE. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:29488–29493. - PubMed
-
- Igarashi P, Somlo S. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:2384–2398. - PubMed
-
- Nauli SM, Alenghat FJ, Luo Y, Williams E, Vassilev P, Li X, Elia AE, Lu W, Brown EM, Quinn SJ, et al. Nat Genet. 2003;33:129–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

