Induced mitotic recombination of p53 in vivo
- PMID: 17360553
- PMCID: PMC1838630
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0607953104
Induced mitotic recombination of p53 in vivo
Abstract
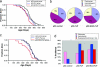
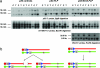
Genetic mosaics produced by FLP/FRT induced mitotic recombination have been widely used in Drosophila to study gene function in development. Recently, the Cre/loxP system has been applied to induce mitotic recombination in mouse embryonic stem cells and in many adult mouse tissues. We have used this strategy to generate a previously undescribed p53 mouse model in which expression of a ubiquitously expressed recombinase in a heterozygous p53 knockout animal produces mitotic recombinant clones homozygous for the p53 mutation. The induction of loss of heterozygosity in a few cells in an otherwise normal tissue mimics genetic aspects of tumorigenesis more closely than existing models and has revealed the possible cell autonomous nature of Wnt3. Our results suggest that inducible mitotic recombination can be used for clonal analysis of mutants in the mouse.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Comment in
-
New mouse models of cancer: single-cell knockouts.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Mar 13;104(11):4245-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700173104. Epub 2007 Mar 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17360508 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Donehower LA, Harvey M, Slagle BL, McArthur MJ, Montgomery CA, Jr, Butel JS, Bradley A. Nature. 1992;356:215–221. - PubMed
-
- Jacks T, Remington L, Williams BO, Schmitt EM, Halachmi S, Bronson RT, Weinberg RA. Curr Biol. 1994;4:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Purdie CA, Harrison DJ, Peter A, Dobbie L, White S, Howie SE, Salter DM, Bird CC, Wyllie AH, Hooper ML, et al. Oncogene. 1994;9:603–609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

