Transgenic LacZ under control of Hec-6st regulatory sequences recapitulates endogenous gene expression on high endothelial venules
- PMID: 17360566
- PMCID: PMC1838643
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0700334104
Transgenic LacZ under control of Hec-6st regulatory sequences recapitulates endogenous gene expression on high endothelial venules
Abstract
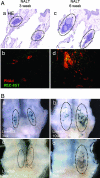
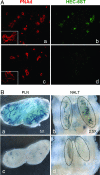
Hec-6st is a highly specific high endothelial venule (HEV) gene that is crucial for regulating lymphocyte homing to lymph nodes (LN). The enzyme is also expressed in HEV-like vessels in tertiary lymphoid organs that form in chronic inflammation in autoimmunity, graft rejection, and microbial infection. Understanding the molecular nature of Hec-6st regulation is crucial for elucidating its function in development and disease. However, studies of HEV are limited because of the difficulties in isolating and maintaining the unique characteristics of these vessels in vitro. The novel pClasper yeast homologous recombination technique was used to isolate from a BAC clone a 60-kb DNA fragment that included the Hec-6st (Chst4) gene with flanking sequences. Transgenic mice were generated with the beta-galactosidase (LacZ) reporter gene inserted in-frame in the exon II of Hec-6st within the isolated BAC DNA fragment. LacZ was expressed specifically on HEV in LN, as indicated by its colocalization with peripheral node vascular addressin. LacZ was increased in nasal-associated lymphoid tissue during development and was reduced in LN and nasal-associated lymphoid tissue by LTbetaR-Ig (lymphotoxin-beta receptor human Ig fusion protein) treatment in a manner identical to the endogenous gene. The transgene was expressed at high levels in lymphoid accumulations with characteristics of tertiary lymphoid organs in the salivary glands of aged mice. Thus, the Hec-6s-LacZ construct faithfully reproduces Hec-6st tissue-specific expression and can be used in further studies to drive expression of reporter or effector genes, which could visualize or inhibit HEV in autoimmunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

