Structure of the Parkin in-between-ring domain provides insights for E3-ligase dysfunction in autosomal recessive Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 17360614
- PMCID: PMC1805599
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0610548104
Structure of the Parkin in-between-ring domain provides insights for E3-ligase dysfunction in autosomal recessive Parkinson's disease
Abstract
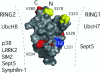
Mutations in Parkin are one of the predominant hereditary factors found in patients suffering from autosomal recessive juvenile Parkinsonism. Parkin is a member of the E3 ubiquitin ligase family that is defined by a tripartite RING1-in-between-ring (IBR)-RING2 motif. In Parkin, the IBR domain has been shown to augment binding of the E2 proteins UbcH7 and UbcH8, and the subsequent ubiquitination of the proteins synphilin-1, Sept5, and SIM2. To facilitate our understanding of Parkin function, the solution structure of the Parkin IBR domain was solved by using NMR spectroscopy. Folding of the IBR domain (residues M327-S378) was found to be zinc dependent, and the structure reveals the domain forms a unique pair scissor-like and GAG knuckle-like zinc-binding sites, different from other zinc-binding motifs such as the RING, LIM, PHD, or B-box motifs. The N terminus of the IBR domain, residues E307-E322, is unstructured. The disease causing mutation T351P causes global unfolding, whereas the mutation R334C causes some structural rearrangement of the domain. In contrast, the protein containing the mutation G328E appears to be properly folded. The structure of the Parkin IBR domain, in combination with mutational data, allows a model to be proposed where the IBR domain facilitates a close arrangement of the adjacent RING1 and RING2 domains to facilitate protein interactions and subsequent ubiquitination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Warner TT, Schapira AH. In: Ann Neurol. 2003. pp. S16–S23. discussion S23–S25. - PubMed
-
- Betarbet R, Sherer TB, Greenamyre JT. Exp Neurol. 2005;191(Suppl 1):S17–S27. - PubMed
-
- Shimura H, Hattori N, Kubo S, Mizuno Y, Asakawa S, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Iwai K, Chiba T, Tanaka K, Suzuki T. Nat Genet. 2000;25:302–305. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka K, Suzuki T, Hattori N, Mizuno Y. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1695:235–247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

