HIV-tat induces formation of an LRP-PSD-95- NMDAR-nNOS complex that promotes apoptosis in neurons and astrocytes
- PMID: 17360663
- PMCID: PMC1805607
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0611699104
HIV-tat induces formation of an LRP-PSD-95- NMDAR-nNOS complex that promotes apoptosis in neurons and astrocytes
Abstract
HIV infection of the central nervous system can result in neurologic dysfunction with devastating consequences in AIDS patients. NeuroAIDS is characterized by neuronal injury and loss, yet there is no evidence that HIV can infect neurons. Here we show that the HIV-encoded protein tat triggers formation of a macromolecular complex involving the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP), postsynaptic density protein-95 (PSD-95), N-methyl-d-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptors, and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) at the neuronal plasma membrane, and that this complex leads to apoptosis in neurons negative as well as positive for NMDA receptors and also in astrocytes. Blockade of LRP-mediated tat uptake, NMDA receptor activation, or neuronal nitric oxide synthase significantly reduces ensuing neuronal apoptosis, suggesting that formation of this complex is an early step in tat toxicity. We also show that the inflammatory chemokine, CCL2, protects against tat toxicity and inhibits formation of the complex. These findings implicate the complex in HIV-induced neuronal apoptosis and suggest therapeutic targets for intervention in the pathogenesis of NeuroAIDS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
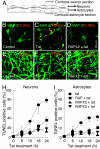
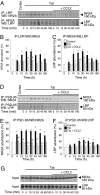
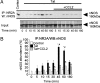
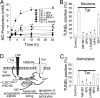
References
-
- Anthony IC, Ramage SN, Carnie FW, Simmonds P, Bell JE. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2005;64:529–536. - PubMed
-
- Ensoli B, Barillari G, Salahuddin SZ, Gallo RC, Wong-Staal F. Nature. 1990;345:84–86. - PubMed
-
- Haughey NJ, Nath A, Mattson MP, Slevin JT, Geiger JD. J Neurochem. 2001;78:457–467. - PubMed
-
- Wang P, Barks JD, Silverstein FS. Neuroscience. 1999;88:585–597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS20752/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AI-051519/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI051519/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- NS11920/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH052974/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5 T32 GM007288/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS45287/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P20RR015592/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS045287/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015592/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH070297/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH075679/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS020752/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH076679/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH070297/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS011920/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH075679/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007288/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

