Identification of IGF2 signaling through phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 3 as a growth-promoting axis in glioblastoma
- PMID: 17360667
- PMCID: PMC1802005
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0611271104
Identification of IGF2 signaling through phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 3 as a growth-promoting axis in glioblastoma
Abstract
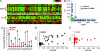
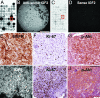
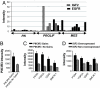
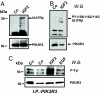
Amplification or overexpression of growth factor receptors is a frequent occurrence in malignant gliomas. Using both expression profiling and in situ hybridization, we identified insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) as a marker for a subset of glioblastomas (GBMs) that lack amplification or overexpression of EGF receptor. Among 165 primary high-grade astrocytomas, 13% of grade IV tumors and 2% of grade III tumors expressed IGF2 mRNA levels >50-fold the sample population median. IGF2-overexpressing tumors frequently displayed PTEN loss, were highly proliferative, exhibited strong staining for phospho-Akt, and belonged to a subclass of GBMs characterized by poor survival. Using a serum-free culture system, we discovered that IGF2 can substitute for EGF to support the growth of GBM-derived neurospheres. The growth-promoting effects of IGF2 were mediated by the insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 and phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 3 (PIK3R3), a regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase that shows genomic gains in some highly proliferative GBM cases. PIK3R3 knockdown inhibited IGF2-induced growth of GBM-derived neurospheres. The current results provide evidence that the IGF2-PIK3R3 signaling axis is involved in promoting the growth of a subclass of highly aggressive human GBMs that lack EGF receptor amplification. Our data underscore the importance of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway for growth of high-grade gliomas and suggest that multiple molecular alterations that activate this signaling cascade may promote tumorigenesis. Further, these findings highlight the parallels between growth factors or receptors that are overexpressed in GBMs and those that support in vitro growth of tumor-derived stem-like cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IGFBP6 controls the expansion of chemoresistant glioblastoma through paracrine IGF2/IGF-1R signaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2018 Sep 19;16(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12964-018-0273-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2018. PMID: 30231881 Free PMC article.
-
Imp2 regulates GBM progression by activating IGF2/PI3K/Akt pathway.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(4):623-33. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1019185. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25719943 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin growth factor-2 binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) is a glioblastoma-specific marker that activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase (PI3K/MAPK) pathways by modulating IGF-2.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 22;286(29):25882-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.178012. Epub 2011 May 25. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21613208 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor tyrosine kinase-Ras-PI 3 kinase-Akt signaling network in glioblastoma multiforme.Med Oncol. 2018 Aug 4;35(9):122. doi: 10.1007/s12032-018-1185-5. Med Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30078108 Review.
-
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling pathway as a therapeutic target in grade IV brain tumors.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2011 Oct;11(8):894-918. doi: 10.2174/156800911797264743. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21861842 Review.
Cited by
-
Variable expression of PIK3R3 and PTEN in Ewing Sarcoma impacts oncogenic phenotypes.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 20;10(1):e0116895. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116895. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25603314 Free PMC article.
-
IGFBP6 controls the expansion of chemoresistant glioblastoma through paracrine IGF2/IGF-1R signaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2018 Sep 19;16(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12964-018-0273-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2018. PMID: 30231881 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosomal Instability and Phosphoinositide Pathway Gene Signatures in Glioblastoma Multiforme.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jan;53(1):621-630. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-9034-9. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25502460 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and Therapeutic Roles of the Insulin Growth Factor System in Glioblastoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 2;10:612385. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.612385. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33604294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential genomic imprinting regulates paracrine and autocrine roles of IGF2 in mouse adult neurogenesis.Nat Commun. 2015 Sep 15;6:8265. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9265. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26369386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Holland EC. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2:120–129. - PubMed
-
- Galli R, Binda E, Orfanelli U, Cipelletti B, Gritti A, De Vitis S, Fiocco R, Foroni C, Dimeco F, Vescovi A. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7011–7021. - PubMed
-
- Sanai N, Alvarez-Buylla A, Berger MS. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:811–822. - PubMed
-
- Nutt C, Louis DN. Cancer of the Nervous System. 2nd Ed. New York: McGraw–Hill; 2005. pp. 837–847.
-
- Phillips HS, Kharbanda S, Chen R, Forrest WF, Soriano RH, Wu TD, Misra A, Nigro JA, Colman H, Soroceanu L, et al. Cancer Cell. 2006;9:157–163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

