Differential gene expression of p27Kip1 and Rb knockout pituitary tumors associated with altered growth and angiogenesis
- PMID: 17361101
- PMCID: PMC2040307
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.6.6.3986
Differential gene expression of p27Kip1 and Rb knockout pituitary tumors associated with altered growth and angiogenesis
Abstract
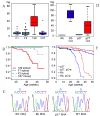
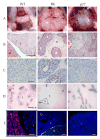
Mice lacking the p27Kip1 Cdk inhibitor, like mice lacking Rb, develop pituitary tumors involving pars intermedia melanotrophs, yet p27(Kip1) tumors are genetically distinct from Rb derived tumors as they exhibit haploid insufficiency. We compared tumors from mice with p27( Kip1) constitutive and tissue specific null mutations to tumors arising in tissue specific Rb knockout mice with the aim of determining whether they are distinguished by quantitative or qualitative differences. The rate of p27Kip1 knockout tumor development was strongly influenced by strain background due to polygenic strain modifiers in the C57BL/6J versus 129S4 strains but, unlike a prior report of Rb mutants, this impacted tumor incidence but not the tumor spectrum. p27Kip1 tumors were oligoclonal or polyclonal based on studies of X-chromosomal inactivation of Dock11. In contrast, Rb null tissue developed monoclonal neoplasms even in the absence of a requirement for Rb mutant clonal selection. Rb null tumors exhibited a higher proliferation rate and developed ischemic necrosis associated with an aberrant vasculature. p27Kip1 null tumors maintained normal vascular density, through a tumor cell dependent mechanism, but were more often hemorrhagic. Gene expression profiles distinguished p27Kip1 from Rb null tumors including significant differences in expression of Rb and E2F signature genes. Rb null tumors expressed higher levels of VEGF which, in other systems, is associated with dilated vessels, ineffective perfusion and tissue hypoxia. Mouse models lacking p27Kip1 and Rb may help us better understand the pathophysiology of MEN syndromes, retinoblastoma and other cancers that disrupt these important cell cycle inhibitors.
Figures


References
-
- Sherr CJ, McCormick F. The RB and p53 pathways in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:103–12. - PubMed
-
- Hu N, Gutsmann A, Herbert DC, Bradley A, Lee WH, Lee EY. Heterozygous Rb-1 delta 20/+mice are predisposed to tumors of the pituitary gland with a nearly complete penetrance. Oncogene. 1994;9:1021–7. - PubMed
-
- Kiyokawa H, Kineman RD, Manova-Todorova KO, Soares VC, Hoffman ES, Ono M, Khanam D, Hayday AC, Frohman LA, Koff A. Enhanced growth of mice lacking the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor function of p27(Kip1) Cell. 1996;85:721–32. - PubMed
-
- Nakayama K, Ishida N, Shirane M, Inomata A, Inoue T, Shishido N, Horii I, Loh DY. Mice lacking p27(Kip1) display increased body size, multiple organ hyperplasia, retinal dysplasia, and pituitary tumors. Cell. 1996;85:707–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
