Botanical dietary supplements gone bad
- PMID: 17362034
- PMCID: PMC2504026
- DOI: 10.1021/tx7000527
Botanical dietary supplements gone bad
Figures


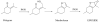

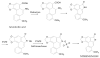
References
-
- Bent S, Ko R. Commonly used herbal medicines in the United States: a review. Am. J. Med. 2004;116:478–485. see comment. - PubMed
-
- Schilter B, Andersson C, Anton R, Constable A, Kleiner J, O’Brien J, Renwick AG, Korver O, Smit F, Walker R, Natural Toxin Task Force of the European Branch of the International Life Sciences, I Guidance for the safety assessment of botanicals and botanical preparations for use in food and food supplements. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003;41:1625–1649. - PubMed
-
- Timbo BB, Ross MP, McCarthy PV, Lin C-TJ. Dietary Supplements in a National Survey: Prevalence of Use and Reports of Adverse Events. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2006;106:1966–1974. - PubMed
-
- Molinari M, Watt KDS, Kruszyna T, Nelson R, Walsh M, Huang WY, Nashan B, Peltekian K. Acute Liver Failure Induced by Green Tea Extracts: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Liver Transpl. 2006;12:1892–1895. - PubMed
-
- Anke J, Ramzan I. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic drug interactions with Kava (Piper methysticum Forst. f.) J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004;93:153–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

