Lipid A modification systems in gram-negative bacteria
- PMID: 17362200
- PMCID: PMC2569861
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.010307.145803
Lipid A modification systems in gram-negative bacteria
Abstract
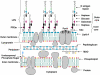
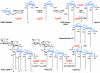
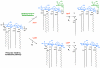
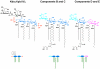
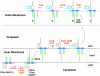
The lipid A moiety of lipopolysaccharide forms the outer monolayer of the outer membrane of most gram-negative bacteria. Escherichia coli lipid A is synthesized on the cytoplasmic surface of the inner membrane by a conserved pathway of nine constitutive enzymes. Following attachment of the core oligosaccharide, nascent core-lipid A is flipped to the outer surface of the inner membrane by the ABC transporter MsbA, where the O-antigen polymer is attached. Diverse covalent modifications of the lipid A moiety may occur during its transit from the outer surface of the inner membrane to the outer membrane. Lipid A modification enzymes are reporters for lipopolysaccharide trafficking within the bacterial envelope. Modification systems are variable and often regulated by environmental conditions. Although not required for growth, the modification enzymes modulate virulence of some gram-negative pathogens. Heterologous expression of lipid A modification enzymes may enable the development of new vaccines.
Figures
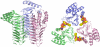
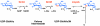



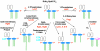
References
-
- Fahy E, Subramaniam S, Brown HA, Glass CK, Merrill AH, Jr., et al. J. Lipid Res. 2005;46:839–62. - PubMed
-
- Brade H, Opal SM, Vogel SN, Morrison DC, editors. Endotoxin in Health and Disease. Marcel Dekker, Inc.; New York: 1999. p. 950.
-
- Galloway SM, Raetz CRH. J. Biol. Chem. 1990;265:6394–402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

