Potato lectin activates basophils and mast cells of atopic subjects by its interaction with core chitobiose of cell-bound non-specific immunoglobulin E
- PMID: 17362264
- PMCID: PMC1941928
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03368.x
Potato lectin activates basophils and mast cells of atopic subjects by its interaction with core chitobiose of cell-bound non-specific immunoglobulin E
Abstract
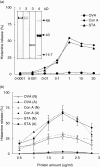
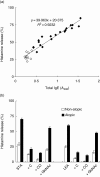
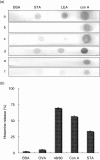
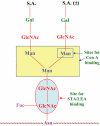
A major factor in non-allergic food hypersensitivity could be the interaction of dietary lectins with mast cells and basophils. Because immunoglobulin E (IgE) contains 10-12% carbohydrates, lectins can activate and degranulate these cells by cross-linking the glycans of cell-bound IgE. The present objective focuses on the effect of potato lectin (Solanum tuberosum agglutinin; STA) for its ability to release histamine from basophils in vitro and mast cells in vivo from non-atopic and atopic subjects. In this study, subjects were selected randomly based on case history and skin prick test responses with food, pollen and house dust mite extracts. Skin prick test (SPT) was performed with STA at 100 microg/ml concentration. Histamine release was performed using leucocytes from non-atopic and atopic subjects and rat peritoneal exudate cells. SPT on 110 atopic subjects using STA showed 39 subjects positive (35%); however, none showed STA-specific IgE; among 20 non-atopic subjects, none were positive by SPT. Maximal histamine release was found to be 65% in atopic subjects (n = 7) compared to 28% in non-atopic subjects (n = 5); the release was inhibited specifically by oligomers of N-acetylglucosamine and correlates well with serum total IgE levels (R(2) = 0.923). Binding of STA to N-linked glycoproteins (horseradish peroxidase, avidin and IgG) was positive by dot blot and binding assay. As potato lectin activates and degranulates both mast cells and basophils by interacting with the chitobiose core of IgE glycans, higher intake of potato may increase the clinical symptoms as a result of non-allergic food hypersensitivity in atopic subjects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Banana lectin (BanLec) induces non-specific activation of basophils and mast cells in atopic subjects.Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018 Nov;50(6):243-253. doi: 10.23822/EurAnnACI.1764-1489.64. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30039691
-
Effect of horse gram lectin (Dolichos biflorus agglutinin) on degranulation of mast cells and basophils of atopic subjects: identification as an allergen.Int Immunopharmacol. 2006 Nov;6(11):1714-22. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2006.07.006. Epub 2006 Aug 4. Int Immunopharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16979126 Clinical Trial.
-
Does skin prick test correlate with basophil-associated mite-specific IgE in atopic children?J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2003;13(1):73-5. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12861857
-
Introduction: basophil histamine release and the diagnosis of food allergy.Allergy Proc. 1993 Jul-Aug;14(4):243-9. doi: 10.2500/108854193778811955. Allergy Proc. 1993. PMID: 7693545 Review.
-
[Treatment of allergic diseases with monoclonal anti-IgE antibody].Nihon Rinsho. 2001 Oct;59(10):2019-22. Nihon Rinsho. 2001. PMID: 11676148 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Recombinant ArtinM activates mast cells.BMC Immunol. 2016 Jul 4;17(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12865-016-0161-0. BMC Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27377926 Free PMC article.
-
The lectin ArtinM induces recruitment of rat mast cells from the bone marrow to the peritoneal cavity.PLoS One. 2010 Mar 22;5(3):e9776. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009776. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20339538 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of mTOR effector phosphoproteins in blood basophils from allergic patients.J Clin Immunol. 2012 Jun;32(3):565-73. doi: 10.1007/s10875-012-9651-x. Epub 2012 Feb 21. J Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22350221 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescent Neoglycoprotein Gold Nanoclusters: Synthesis and Applications in Plant Lectin Sensing and Cell Imaging.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2018 Nov 12;13(1):360. doi: 10.1186/s11671-018-2772-2. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2018. PMID: 30421263 Free PMC article.
-
Immune response to snake envenoming and treatment with antivenom; complement activation, cytokine production and mast cell degranulation.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013 Jul 25;7(7):e2326. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002326. Print 2013. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013. PMID: 23936562 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Prussin C, Metcalfe DD. IgE, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111:S486–94. - PubMed
-
- Van Drunen CM, Fokkens WJ. Basophils and mast cells at the center of the immunological response. Allergy. 2006;61:273–5. - PubMed
-
- Gibbs BF. Human basophils as effectors and immunomodulators of allergic inflammation and innate immunity. Clin Exp Med. 2005;5:43–9. - PubMed
-
- Shibasaki M, Sumazaki R, Isoyama S, Takita H. Interactions of lectins with human IgE: IgE-binding property and histamine-releasing activity of twelve plant lectins. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1992;98:18–25. - PubMed
-
- Haas H, Falcone FH, Schramm G. Dietary lectins can induce in vitro release of IL-4 and IL-13 from human basophils. Eur J Immunol. 1999;29:918–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

