Partial urethral obstruction of rabbit urinary bladder: stereological evidence that the increase in muscle content is mostly driven by changes in number, rather than size, of smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 17362488
- PMCID: PMC2100292
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2007.00702.x
Partial urethral obstruction of rabbit urinary bladder: stereological evidence that the increase in muscle content is mostly driven by changes in number, rather than size, of smooth muscle cells
Abstract
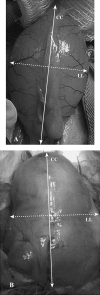
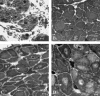
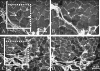
The effects of partial urethral obstruction on the detrusor muscle of rabbit urinary bladder were investigated using stereological sampling and estimation tools. Twelve female Norfolk rabbits (2.5-3.0 kg body weight) were divided into four groups: 3, 7 and 12 weeks after surgical intervention to produce a standard partial obstruction and unobstructed controls. Following removal, bladder axes (craniocaudal, dorsoventral and laterolateral) and organ weights were recorded. Bladders were prepared for light microscopy by multistage random sampling procedures. Stereological methods were used to estimate the volume of muscle and the packing density and total number of myocyte nuclei in each bladder. We also estimated mean myocyte volume and the mean cross-sectional area and length of myocytes. Group comparisons were made by one-way analysis of variance. Changes in bladder axes were mainly laterolateral and craniocaudal. Mean bladder weight increased roughly six-fold by 3 weeks and 17-fold by 12 weeks and was accompanied, on average, by 12- and 33-fold increases in total muscle volume. These variables did not differ at 3 and 7 weeks post-obstruction. Increases in muscle content were not accompanied by changes in packing densities but were associated with increases in the total numbers of myocyte nuclei (13-fold by 3 weeks, 28-fold by 12 weeks). Mean myocyte volume did not vary significantly between groups but cells in obstructed groups were shorter and wider. These findings support the notion that partial outflow obstruction leads to an increase in the number, but not mean volume, of myocytes. If due solely to myocyte mitosis, the total of 43 x 10(8) cells found at 12 weeks could be generated by the original complement of 15 x 10(7) cells if an average of only 2.1 x 10(6) new cells was produced every hour. In reality, even this modest proliferation rate is unlikely to be achieved because myocyte proliferation rates are very low and it is possible that new myocytes can arise by differentiation of mesenchymal or other precursor cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Partial urethral obstruction: ATF3 and p-c-Jun are involved in the growth of the detrusor muscle and its motor innervation.Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2011 Feb;45(1):30-8. doi: 10.3109/00365599.2010.521188. Epub 2010 Oct 25. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 20969496
-
Rabbit urinary bladder blood flow changes during the initial stage of partial outlet obstruction.J Urol. 2000 Oct;164(4):1390-7. J Urol. 2000. PMID: 10992421
-
The response of smooth muscle cells in the rabbit urinary bladder to outflow obstruction.Invest Urol. 1975 May;12(6):494-502. Invest Urol. 1975. PMID: 1120643
-
Effects of chronic partial outlet obstruction on blood flow and oxygenation of the rat bladder.J Urol. 2002 Mar;167(3):1508-12. J Urol. 2002. PMID: 11832779
-
Serosal thickening, smooth muscle cell growth, and phenotypic changes in the rabbit bladder wall during outflow obstruction and regeneration.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;462:63-81. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4737-2_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999. PMID: 10599414 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Austin JC, Chacko SK, DiSanto M, Canning DA, Zderic AS. A male murine model of partial outlet obstruction reveals changes in detrusor morphology, contractility and myosin isoform expression. J Urol. 2004;172:1524–1528. - PubMed
-
- Brent L, Stephens DF. The response of smooth muscle cells in the rabbit urinary bladder to outflow obstruction. Invest Urol. 1975;12:494–502. - PubMed
-
- Brüel A, Nyengaard JR. Design-based stereological estimation of the total number of cardiac myocytes in histological sections. Basic Res Cardiol. 2005;100:311–319. - PubMed
-
- Buoro S, Ferrarese P, Chiavegato A, et al. Myofibroblast-derived smooth muscle cells during remodelling of rabbit urinary bladder wall induced by partial outflow obstruction. Lab Invest. 1993;69:589–602. - PubMed
-
- Burkhard FC, Monastyrskaya K, Studer UE. Smooth muscle membrane organization in the normal and dysfunctional human urinary bladder: a structural analysis. Neurourol Urodyn. 2005;24:128–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

