Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1b is required for zebrafish primordial germ cell migration and survival
- PMID: 17362906
- PMCID: PMC1964797
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.02.015
Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1b is required for zebrafish primordial germ cell migration and survival
Abstract
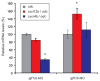
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling is a critical regulator of somatic growth during fetal and adult development, primarily through its stimulatory effects on cell proliferation and survival. IGF signaling is also required for development of the reproductive system, although its precise role in this regard remains unclear. We have hypothesized that IGF signaling is required for embryonic germline development, which requires the specification and proliferation of primordial germ cells (PGCs) in an extragonadal location, followed by directed migration to the genital ridges. We tested this hypothesis using loss-of-function studies in the zebrafish embryo, which possesses two functional copies of the Type-1 IGF receptor gene (igf1ra, igf1rb). Knockdown of IGF1Rb by morpholino oligonucleotides (MO) results in mismigration and elimination of primordial germ cells (PGCs), resulting in fewer PGCs colonizing the genital ridges. In contrast, knockdown of IGF1Ra has no effect on PGC migration or number despite inducing widespread somatic cell apoptosis. Ablation of both receptors, using combined MO injections or overexpression of a dominant-negative IGF1R, yields embryos with a PGC-deficient phenotype similar to IGF1Rb knockdown. TUNEL analyses revealed that mismigrated PGCs in IGF1Rb-deficient embryos are eliminated by apoptosis; overexpression of an antiapoptotic gene (Bcl2l) rescues ectopic PGCs from apoptosis but fails to rescue migration defects. Lastly, we show that suppression of IGF signaling leads to quantitative changes in the expression of genes encoding CXCL-family chemokine ligands and receptors involved in PGC migration. Collectively, these data suggest a novel role for IGF signaling in early germline development, potentially via cross-talk with chemokine signaling pathways.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Paracrine insulin-like growth factor signaling influences primordial germ cell migration: in vivo evidence from the zebrafish model.Endocrinology. 2008 Oct;149(10):5035-42. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0534. Epub 2008 Jun 19. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18566124
-
Zebrafish Staufen1 and Staufen2 are required for the survival and migration of primordial germ cells.Dev Biol. 2006 Apr 15;292(2):393-406. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.01.014. Epub 2006 Mar 2. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16513105
-
Heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans modulate migration and survival in zebrafish primordial germ cells.Theriogenology. 2014 Jun;81(9):1275-85.e1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2014.02.009. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Theriogenology. 2014. PMID: 24629592
-
Primordial germ cells: what does it take to be alive?Mol Reprod Dev. 2004 May;68(1):1-4. doi: 10.1002/mrd.20056. Mol Reprod Dev. 2004. PMID: 15039942 Review.
-
Germ line development in fishes.Int J Dev Biol. 1999;43(7):745-60. Int J Dev Biol. 1999. PMID: 10668983 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into early ontogenesis: characterization of stress and development key genes of pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) in vivo and in vitro.Fish Physiol Biochem. 2021 Apr;47(2):515-532. doi: 10.1007/s10695-021-00929-6. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33559015 Free PMC article.
-
Noncanonical translation via deadenylated 3' UTRs maintains primordial germ cells.Nat Chem Biol. 2018 Sep;14(9):844-852. doi: 10.1038/s41589-018-0098-0. Epub 2018 Jul 9. Nat Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29988067 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic architecture of sex determination in fish: applications to sex ratio control in aquaculture.Front Genet. 2014 Sep 29;5:340. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00340. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 25324858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stanniocalcin 1a regulates organismal calcium balance and survival by suppressing Trpv6 expression and inhibiting IGF signaling in zebrafish.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 26;14:1276348. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1276348. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37964974 Free PMC article.
-
cables1 is required for embryonic neural development: molecular, cellular, and behavioral evidence from the zebrafish.Mol Reprod Dev. 2011 Jan;78(1):22-32. doi: 10.1002/mrd.21263. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Mol Reprod Dev. 2011. PMID: 21268180 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abuzzahab MJ, Schneider A, Goddard A, Grigorescu F, Lautier C, Keller E, Kiess W, Klammt J, Kratzsch J, Osgood D, Pfaffle R, Raile K, Seidel B, Smith RJ, Chernausek SD. IGF-I receptor mutations resulting in intrauterine and postnatal growth retardation. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2211–22. - PubMed
-
- Akekawatchai C, Holland JD, Kochetkova M, Wallace JC, McColl SR. Transactivation of CXCR4 by the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) in human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:39701–8. - PubMed
-
- Anderson R, Fassler R, Georges-Labouesse E, Hynes RO, Bader BL, Kreidberg JA, Schaible K, Heasman J, Wylie C. Mouse primordial germ cells lacking beta1 integrins enter the germline but fail to migrate normally to the gonads. Development. 1999;126:1655–64. - PubMed
-
- Baker J, Hardy MP, Zhou J, Bondy C, Lupu F, Bellve AR, Efstratiadis A. Effects of an IGF1 gene null mutation on mouse reproduction. Mol Endocrinol. 1996;10:903–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

