Neurokinins enhance excitability in capsaicin-responsive DRG neurons
- PMID: 17362934
- PMCID: PMC1995809
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.01.038
Neurokinins enhance excitability in capsaicin-responsive DRG neurons
Abstract
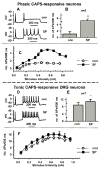
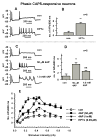
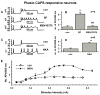
Neurokinins released by capsaicin-responsive (C-R) dorsal root ganglia neurons (DRG) may control firing in these neurons by an autofeedback mechanism. Here we used patch clamp techniques to examine the effects of neurokinins on firing properties of dissociated DRG neurons of male rats. In C-R neurons that generated only a few action potentials (APs, termed phasic) in response to long depolarizing current pulses (600 ms), substance P (SP, 0.5 microM) lowered the AP threshold by 11.0+/-0.3 mV and increased firing from 1.1+/-0.7 APs to 5.2+/-0.6 APs. In C-R tonic neurons that fire multiple APs, SP elicited smaller changes in AP threshold (6.0+/-0.1 mV reduction) and the number of APs (11+/-1 vs. 9+/-1 in control). The effects of SP were similar to the effect of heteropodatoxin II (0.05 microM) or low concentrations of 4-aminopyridine (50 microM) that block A-type K(+) currents. A selective NK(2) agonist, [betaAla(8)]-neurokinin A (4-10) (0.5 microM), mimicked the effects of SP. The effects of SP in C-R phasic neurons were fully reversed by an NK(2) receptor antagonist (MEN10376, 0.5 microM) but only partially by a protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor (bisindolylmaleimide, 0.5 microM). An NK(3)-selective agonist ([MePhe(7)]-neurokinin B, 0.5 microM), an NK(1)-selective agonist ([Sar(9), Met(11)]-substance P, 0.5 microM) or activation of PKC with phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate (0.5 microM) did not change firing. Our data suggest that the excitability of C-R phasic afferent neurons is increased by activation of NK(2) receptors and intracellular signaling mediated only in part by PKC.
Figures



References
-
- Abdulla FA, Stebbing MJ, Smith PA. Effects of substance P on excitability and ionic currents of normal and axotomized rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 2001;13:545–652. - PubMed
-
- Andersson KE. The overactive bladder: pharmacologic basis of drug treatment. Urol. 1997;50:74–84. - PubMed
-
- Boland LM, Jackson KA. Protein kinase C inhibits Kv1.1 potassium channel function. Am J Physiol. 1999;277:C100–C110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

