Alpha1-adrenergic receptors mediate the locomotor response to systemic administration of (+/-)-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) in rats
- PMID: 17363047
- PMCID: PMC1976288
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2007.02.006
Alpha1-adrenergic receptors mediate the locomotor response to systemic administration of (+/-)-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) in rats
Abstract
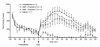
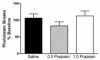
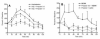
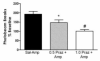
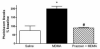
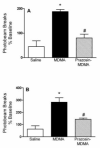
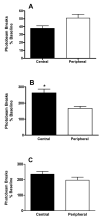
The recreational drug 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, ecstasy) increases locomotor activity when administered to rats. Although the published pharmacology of MDMA has focused almost exclusively on the roles of serotonin and dopamine, in vitro studies indicate that MDMA induces serotonin and norepinephrine release with equal potency. The present experiments tested the hypothesis that blockade of alpha(1)-adrenoceptors with systemic or local administration of the antagonist prazosin would attenuate the locomotor response to systemic administration of (+/-)-MDMA. Pretreatment with systemic prazosin (0.5 mg/kg) or microinjections into either the prefrontal cortex or ventral tegmental area completely blocked the locomotor stimulant effects of 5 mg/kg (+/-)-MDMA, assessed using a computerized Behavioral Pattern Monitor. Prazosin was more potent in blocking the locomotor stimulant effects of (+/-)-MDMA than a 2 mg/kg dose of (+)-amphetamine that produced a similar locomotor activity increase. These results indicate that activation of alpha(1)-adrenoceptors in both the prefrontal cortex and ventral tegmental areas modulates the locomotor response to MDMA.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson GM, III, Braun G, Braun U, Nichols DE, Shulgin AT. Absolute configuration and psychotomimetic activity. NIDA Res Monogr. 1978:8–15. - PubMed
-
- Arnt J. Differential effects of classical and newer antipsychotics on the hypermotility induced by two dose levels of (+)-amphetamine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995;283:55–62. - PubMed
-
- Bankson MG, Cunningham KA. Pharmacological studies of the acute effects of (+)-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine on locomotor activity: role of 5- HT(1B/1D) and 5-HT(2) receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002;26:40–52. - PubMed
-
- Blanc G, Trovero F, Vezina P, Herve D, Godeheu AM, Glowinski J, Tassin JP. Blockade of prefronto-cortical alpha 1-adrenergic receptors prevents locomotor hyperactivity induced by subcortical (+)-amphetamine injection. Eur J Neurosci. 1994;6:293–298. - PubMed
-
- Blendy JA, Perry DC, Pabreza LA, Kellar KJ. Electroconvulsive shock increases alpha 1b- but not alpha 1a-adrenoceptor binding sites in rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1991;57:1548–1555. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

