Characterization of a thromboembolic photochemical model of repeated stroke in mice
- PMID: 17363066
- PMCID: PMC2735862
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.01.018
Characterization of a thromboembolic photochemical model of repeated stroke in mice
Abstract
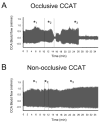
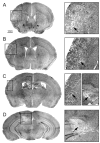
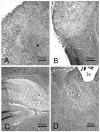
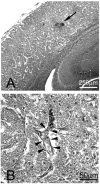
Many stroke research groups utilize the model of middle cerebral artery occlusion induced by insertion of an intraluminal thread, owing to its pragmatism and reliability of cerebral infarct generation. However, 75% of stroke cases result from a thromboembolic event and 10% from occlusive atherothrombosis in situ. Here, we characterize a mouse model of repeated thromboembolic stroke, which closely mimics the intravascular pathophysiology of arterial thrombus generation from an atherosclerotic plaque, and subsequent release of a thrombus into the cerebral circulation as an embolus. Common carotid artery thrombosis (CCAT) was induced photochemically leading to non-occlusive platelet aggregation in C57/BL6 male mice (n=35), and was followed by mechanical assistance to facilitate release of the thrombus (MRT) and thus promote embolism. Six experimental groups, differing by changes in the surgical protocol, were used for the purpose of determining which such procedure yielded the most reliable and consistent brain infarct volumes with the lowest mortality at 3 days after surgery. The group which best satisfied these conditions was a double insult group which consisted of animals that underwent CCAT for 2 min by means of argon laser irradiation (514.5 nm) at an intensity of ca. 130 W/cm(2), with concomitant injection of erythrosin B (EB) (35 mg/kg infused over those same 2 min), followed by MRT 1 min later; the entire procedure was repeated 24h later. This group showed a percent of brain lesion volume of 15+/-4% (mean+/-S.D.) with no associated 3-day mortality. Compared to a single insult group which sustained a percent brain lesion volume of 7+/-3%, there was a statistically significant (p<0.05) increase in the volume of infarction in the double-insult group.
Figures

References
-
- NINDS; The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Effect of intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator on ischemic stroke lesion size measured by computed tomography. Stroke. 2000;31:2912–2919. - PubMed
-
- Asahi M, Asahi K, Jung JC, del Zoppo GJ, Fini ME, Lo EH. Role for matrix metalloproteinase 9 after focal cerebral ischemia: effects of gene knockout and enzyme inhibition with BB-94. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20:1681–1689. - PubMed
-
- Beech JS, Williams SC, Campbell CA, Bath PM, Parsons AA, Hunter AJ, Menon DK. Further characterisation of a thromboembolic model of stroke in the rat. Brain Res. 2001;895:18–24. - PubMed
-
- Belayev L, Busto R, Zhao W, Fernandez G, Ginsberg MD. Middle cerebral artery occlusion in the mouse by intraluminal suture coated with poly-L-lysine: neurological and histological validation. Brain Res. 1999;833:181–190. - PubMed
-
- Bonventre JV, Huang Z, Taheri MR, O’Leary E, Li E, Moskowitz MA, Sapirstein A. Reduced fertility and postischaemic brain injury in mice deficient in cytosolic phospholipase A2. Nature. 1997;390:622–625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

