Balancing autoaggressive and protective T cell responses
- PMID: 17363216
- PMCID: PMC2700848
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2007.02.002
Balancing autoaggressive and protective T cell responses
Abstract
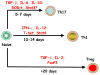
A finely orchestrated balance between activating and inhibitory signals is fundamental for the ability of the immune system to effectively attack and eliminate pathogenic microbes but to not react against self-antigens. Derangements of this balance underlie the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Conversely, elucidating the mechanisms of this balance may provide rational strategies for manipulating it in order to enhance the efficacy of vaccines and tumor immunotherapy. One of the clearest illustrations of precise regulation is in the generation of effector and regulatory T cells. In order to analyze the mechanisms of this regulation, we have developed a transgenic mouse model in which a single population of T cells reacts against its known cognate antigen in vivo. Here we summarize our studies with this experimental model, illustrating the sequence of T cell responses that develop and attempting to dissect the stimuli that control these responses.
Figures
References
-
- Lohr J, Knoechel B, Kahn E, Abbas AK. The role of B7 in T cell tolerance. J Immunol. 2004;173:5028–5035. - PubMed
-
- Kearney ER, Pape KA, Loh DY, Jenkins MK. Visualization of peptide-specific T cell immunity and peripheral tolerance induction in vivo. Immunity. 1994;1:327–339. - PubMed
-
- Perez VL, Van Parijs L, Biuckians A, Zheng XX, Strom TB, Abbas AK. Induction of peripheral T cell tolerance in vivo requires CTLA-4 engagement. Immunity. 1997;6:411–417. - PubMed
-
- Knoechel B, Lohr J, Zhu S, Wong L, Hu D, Ausubel L, Abbas AK. Functional and molecular comparison of anergic and regulatory T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 2006;176:6473–6483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

