Potassium initiates vasodilatation induced by a single skeletal muscle contraction in hamster cremaster muscle
- PMID: 17363384
- PMCID: PMC2075172
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.130013
Potassium initiates vasodilatation induced by a single skeletal muscle contraction in hamster cremaster muscle
Abstract
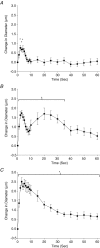
The rapid onset of vasodilatation within seconds of a single contraction suggests that the vasodilators involved may be products of skeletal muscle activation, such as potassium (K(+)). To test the hypothesis that K(+) was in part responsible for the rapid dilatation produced by muscle contraction we stimulated four to five skeletal muscle fibres in the anaesthetized hamster cremaster preparation in situ and measured the change in diameter of arterioles at a site of overlap with the stimulated muscle fibres before and after a single contraction stimulated over a range of stimulus frequencies (4, 10, 20, 30, 40, 60 and 80 Hz; 250 ms train duration). Muscle fibres were stimulated in the absence and presence of an inhibitor of a source of K(+), the voltage dependent K(+) channel inhibitor 3,4-diaminopyridine (DAP, 3 x 10(-4) M) and inhibitors of the K(+) dilatory signal transduction pathway, either a Na(+) K(+)-ATPase inhibitor (ouabain; 10(-4) M) or an inward rectifying K(+) channel inhibitor (barium chloride, BaCl(2); 5 x 10(-5) M). We observed significant inhibitions of the rapid dilatation at all stimulus frequencies with each inhibitor. The dilatory event at 4 s was significantly inhibited at all stimulus frequencies by an average of 65.7 +/- 3.6%, 58.8 +/- 6.1% and 64.4 +/- 2.1% in the presence DAP, ouabain and BaCl(2), respectively. These levels of inhibition did not correlate with non-specific changes in force generation by skeletal muscle measured in vitro. Therefore, our data support that K(+) is involved in the rapid dilatation in response to a single muscle contraction across a wide range of stimulus frequencies.
Figures



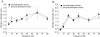
References
-
- Amberg GC, Koh SD, Imaizumi Y, Ohya S, Sanders KM. A-type potassium currents in smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003;284:C583–C595. - PubMed
-
- Baez S. An open cremaster muscle preparation for the study of blood vessels by in vivo microscopy. Microvasc Res. 1973;5:384–394. - PubMed
-
- Beach JM, McGahren ED, Duling BR. Capillaries and arterioles are electrically coupled in hamster cheek pouch. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 1998;275:H1489–H1496. - PubMed
-
- Beaune B, Fellmann N, Villie F, Marcollet M, Coudert J. Effects of orchiectomy on EDL muscle ultrastructure and energy-supplying enzymes in growing male guinea pigs. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 1994;266:C143–C148. - PubMed
-
- Berg BR, Cohen KD, Sarelius IH. Direct coupling between blood flow and metabolism at the capillary level in striated muscle. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 1997;272:H2693–H2700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

