Dynamics of the readily releasable pool during post-tetanic potentiation in the rat calyx of Held synapse
- PMID: 17363387
- PMCID: PMC2075193
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.127365
Dynamics of the readily releasable pool during post-tetanic potentiation in the rat calyx of Held synapse
Abstract
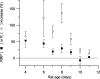
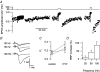
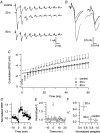
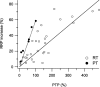
The size of the readily releasable pool (RRP) of vesicles was measured in control conditions and during post-tetanic potentiation (PTP) in a large glutamatergic terminal called the calyx of Held. We measured excitatory postsynaptic currents evoked by a high frequency train of action potentials in slices of 4-11-day-old rats. After a tetanus the cumulative release during such a train was enlarged by approximately 50%, indicating that the size of the RRP was increased. The amount of enhancement depended on the duration and frequency of the tetanus and on the age of the rat. After the tetanus, the size of the RRP decayed more slowly (t(1/2)=10 versus 3 min) back to control values than the release probability. This difference was mainly due to a very fast initial decay of the release probability, which had a time constant compatible with an augmentation phase (tau approximately 30 s). The overall decay of PTP at physiological temperature was not different from room temperature, but the increase in release probability (P(r)) was restricted to the first minute after the tetanus. Thereafter PTP was dominated by an increase in the size of the RRP. We conclude that due to the short lifetime of the increase in release probability, the contribution of the increase in RRP size during post-tetanic potentiation is more significant at physiological temperature.
Figures



References
-
- Awatramani GB, Price GD, Trussell LO. Modulation of transmitter release by presynaptic resting potential and background calcium levels. Neuron. 2005;48:109–121. - PubMed
-
- Bollmann JH, Sakmann B, Borst JGG. Calcium sensitivity of glutamate release in a calyx-type terminal. Science. 2000;289:953–957. - PubMed
-
- Borst JGG, Sakmann B. Calcium influx and transmitter release in a fast CNS synapse. Nature. 1996;383:431–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

