Reduction of arthritis following intra-articular administration of an adeno-associated virus serotype 5 expressing a disease-inducible TNF-blocking agent
- PMID: 17363402
- PMCID: PMC1955149
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.064519
Reduction of arthritis following intra-articular administration of an adeno-associated virus serotype 5 expressing a disease-inducible TNF-blocking agent
Abstract
Background: In the context of preclinical development, we studied the potential of intra-articular gene delivery using a recombinant adeno-associated virus 5 (rAAV5) encoding a chimeric human tumour necrosis factoralpha (TNFalpha) soluble receptor I linked to a mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain Fc portion (TNF receptor I; TNFRI-Ig).
Methods: Expression was under control of a nuclear factor kappa B (NFkappaB)-responsive promoter and compared with a cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter (rAAV5.NFkappaB-TNFRI-Ig and rAAV5.CMV-TNFRI-Ig, respectively).
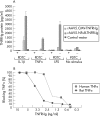
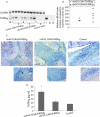
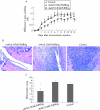
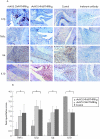
Results: Fibroblast-like synoviocytes transduced in vitro with rAAV5.NFkappaB-TNFRI-Ig were able to produce TNFRI-Ig protein in response to several stimuli, and this was inhibited upon treatment with a specific NFkappaB blocking agent. A bioassay revealed that the synthesised TNFRI-Ig was bioactive, showing a higher affinity for human than for rat TNFalpha. Transcription of the transgene and protein production were detectable in joints injected with both constructs. No dissemination of the vector was observed outside the joints. A significant reduction in paw swelling was seen in rats treated with rAAV5.NFkappaB-TNFRI-Ig. This clinical effect was accompanied by a decrease in pro-inflammatory cytokine levels and an increase in IL10 expression in the synovium.
Conclusion: These results provide evidence that intra-articular gene therapy using rAAV5 encoding TNFRI-Ig may be a safe and feasible approach for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. The higher affinity for human TNFalpha suggests that in patients with rheumatoid arthritis the therapeutic effect might be even more pronounced than in rat adjuvant arthritis.
Similar articles
-
Preclinical Potency and Biodistribution Studies of an AAV 5 Vector Expressing Human Interferon-β (ART-I02) for Local Treatment of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 24;10(6):e0130612. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130612. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26107769 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation-inducible anti-TNF gene expression mediated by intra-articular injection of serotype 5 adeno-associated virus reduces arthritis.J Gene Med. 2007 Jul;9(7):596-604. doi: 10.1002/jgm.1053. J Gene Med. 2007. PMID: 17514770
-
Enhanced gene transfer to arthritic joints using adeno-associated virus type 5: implications for intra-articular gene therapy.Ann Rheum Dis. 2005 Dec;64(12):1677-84. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.035063. Epub 2005 May 5. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. PMID: 15878906 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Delivery to Joints by Intra-Articular Injection.Hum Gene Ther. 2018 Jan;29(1):2-14. doi: 10.1089/hum.2017.181. Hum Gene Ther. 2018. PMID: 29160173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenoviral transgene delivery provides an approach to identifying important molecular processes in inflammation: evidence for heterogenecity in the requirement for NFkappaB in tumour necrosis factor production.Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Nov;59 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):i54-9. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.suppl_1.i54. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000. PMID: 11053090 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Molecular tools to remodel osteoarthritic articular cartilage : growth, transcription, and signaling factors].Orthopade. 2009 Nov;38(11):1063-70. doi: 10.1007/s00132-009-1495-6. Orthopade. 2009. PMID: 19876615 German.
-
Modulation of immune and inflammatory responses on experimental arthritis following intraarticular gene transfer of tumor necrosis factor receptor-immunoglobulin Fc.Rheumatol Int. 2012 Sep;32(9):2605-14. doi: 10.1007/s00296-011-1974-z. Epub 2011 Jul 21. Rheumatol Int. 2012. PMID: 21833532
-
Assembly PCR synthesis of optimally designed, compact, multi-responsive promoters suited to gene therapy application.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 8;6:29388. doi: 10.1038/srep29388. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27387837 Free PMC article.
-
Local expression of tumor necrosis factor-receptor 1:immunoglobulin G can induce salivary gland dysfunction in a murine model of Sjögren's syndrome.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(6):R189. doi: 10.1186/ar2888. Epub 2009 Dec 14. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 20003451 Free PMC article.
-
Computational design and application of endogenous promoters for transcriptionally targeted gene therapy for rheumatoid arthritis.Mol Ther. 2009 Nov;17(11):1877-87. doi: 10.1038/mt.2009.182. Epub 2009 Aug 18. Mol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19690516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tak P P, Bresnihan B. The pathogenesis and prevention of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis: advances from synovial biopsy and tissue analysis. Arthritis Rheum 2000432619–2633. - PubMed
-
- Gomez‐Reino J J, Carmona L, Valverde V R, Mola E M, Montero M D. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors may predispose to significant increase in tuberculosis risk: a multicenter active‐surveillance report. Arthritis Rheum 2003482122–2127. - PubMed
-
- Adriaansen J, Vervoordeldonk M J, Tak P P. Gene therapy as a therapeutic approach for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: innovative vectors and therapeutic genes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 200645656–668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical