Rapid and early virological response to chronic hepatitis C treatment with IFN alpha2b or PEG-IFN alpha2b plus ribavirin in HIV/HCV co-infected patients
- PMID: 17363475
- PMCID: PMC1955519
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2006.106690
Rapid and early virological response to chronic hepatitis C treatment with IFN alpha2b or PEG-IFN alpha2b plus ribavirin in HIV/HCV co-infected patients
Abstract
Background and aims: An algorithm based on a 2 log(10) decline in hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA at week (W) 12 has been proposed in US and European recommendations for the management of patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with pegylated-interferon and ribavirin.
Methods: We examined rapid virological response (RVR; at W2 and W4 after the initiation of therapy) in HIV/HCV co-infected patients. Using HCV RNA measurements (Versant HCV RNA 3.0, Cobas Amplicor HCV 2.0), RVR was studied in 323 patients from the ANRS HC02 RIBAVIC trial, comparing interferon alpha2b 3 MU x3/week with pegylated interferon alpha2b 1.5 microg/kg/week, each combined with ribavirin 800 mg/day over 48 weeks.
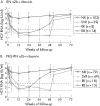
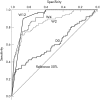
Results: The best positive and negative predictive values of sustained virological response (SVR) were obtained with an undetectable HCV RNA at W4 (97%) and with more than a 2 log(10) decrease at W12 (99%), respectively. Prediction of non-SVR was obtained in all patients by using HCV RNA cut-off levels above 460,000 IU/ml at W4 and above 39,000 UI/ml at W12 irrespective of the HCV genotype and arm of treatment.
Conclusion: We propose a new algorithm based on RVR thresholds using HCV RNA that allows for excellent prediction of non-SVR as early as W4.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
Similar articles
-
Undetectable hepatitis C virus RNA at week 4 as predictor of sustained virological response in HIV patients with chronic hepatitis C.AIDS. 2008 Jan 2;22(1):15-21. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3282f1da99. AIDS. 2008. PMID: 18090387
-
Open, randomized, multicentre italian trial on PEG-IFN plus ribavirin versus PEG-IFN monotherapy for chronic hepatitis C in HIV-coinfected patients on HAART.Antivir Ther. 2005;10(2):309-17. Antivir Ther. 2005. PMID: 15865225 Clinical Trial.
-
Predictive value of rapid virological response and early virological response on sustained virological response in HCV patients treated with pegylated interferon alpha-2a and ribavirin.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007 Jun;22(6):832-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.04904.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. PMID: 17565637
-
Optimizing outcomes in patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 or 4.Antivir Ther. 2008;13 Suppl 1:9-16. Antivir Ther. 2008. PMID: 18432158 Review.
-
Pegylated interferon-α2a and ribavirin versus pegylated interferon-α2b and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C : a meta-analysis.Drugs. 2013 Mar;73(3):263-77. doi: 10.1007/s40265-013-0027-1. Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23436591 Review.
Cited by
-
Antiviral treatment for chronic hepatitis C in patients with human immunodeficiency virus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jan 20;2010(1):CD004888. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004888.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. PMID: 20091566 Free PMC article.
-
Fast hepatitis C virus RNA elimination and NS5A redistribution by NS5A inhibitors studied by a multiplex assay approach.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(6):3482-92. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00223-15. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25845863 Free PMC article.
-
Pegylated interferon 2a and 2b in combination with ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C in HIV infected patients.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2008 Aug;4(4):789-96. doi: 10.2147/tcrm.s2093. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2008. PMID: 19209261 Free PMC article.
-
Coinfection with hepatitis C virus and human immunodeficiency virus: virological, immunological, and clinical outcomes.J Virol. 2009 Aug;83(15):7366-74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00191-09. Epub 2009 May 6. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19420073 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Rapid virological response to peginterferon alfa and ribavirin treatment of chronic hepatitis C predicts sustained virological response and relapse in genotype 1 patients.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2009 Mar;2(2):91-7. doi: 10.1177/1756283X08101217. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 21180537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lauer G, Walker B. Hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 200134541–52. - PubMed
-
- Pol S, Vallet‐Pichard A, Fontaine H. Hepatitis C and HIV co‐infection at the era of HAART. J Viral Hepat 200291–8. - PubMed
-
- Cacoub P, Geffray L, Rosenthal E, for the Joint Study Group on Hepatitis C Virus of the French National Society of Internal Medicine and the French Society of Infectious Diseases (GERMIVIC Study Group) et al Mortality among HIV‐infected patients with cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma due to HCV in French departments of internal medicine/infectious diseases, in 1995 and 1997. Clin Infect Dis 2001321207–1214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials