Regulation of Toll-like receptor-mediated inflammatory response by complement in vivo
- PMID: 17363730
- PMCID: PMC1896115
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-12-063636
Regulation of Toll-like receptor-mediated inflammatory response by complement in vivo
Erratum in
- Blood. 2007 Dec 1;110(12):3841
Abstract
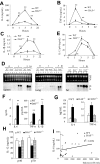
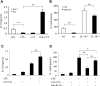
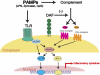
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and complement are 2 components of innate immunity that are critical for first-line host defense and elicitation of adaptive immune responses. Many pathogen-associated molecular patterns activate both TLR and complement, but whether and how these 2 systems, when coactivated in vivo, interact with each other has not been well studied. We demonstrate here a widespread regulation of TLR signaling by complement in vivo. The TLR ligands lipopolysacharride (TLR4), zymosan (TLR2/6), and CpG oligonucleotide (TLR9) caused, in a complement-dependent manner, strikingly elevated plasma interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), and IL-1beta, and/or decreased plasma IL-12 levels in mice deficient in the membrane complement inhibitor decay-accelerating factor (DAF). A similar outcome was observed in wild-type mice cotreated with the TLR ligands and cobra venom factor, a potent complement activator. The regulatory effect of complement on TLR-induced cytokine production in vivo was mediated by the anaphylatoxin receptors C5aR and C3aR. Additionally, changes in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced cytokine production in DAF-deficient mice correlated with increased mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-kappaB activation in the spleen. These results reveal a strong interaction between complement and TLR signaling in vivo and suggest a novel mechanism by which complement promotes inflammation and modulates adaptive immunity.
Figures
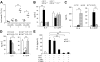
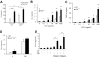


References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Walport MJ. Complement. First of two parts. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1058–1066. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:816–825. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Carroll MC. The complement system in regulation of adaptive immunity. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:981–986. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

