Granzyme H destroys the function of critical adenoviral proteins required for viral DNA replication and granzyme B inhibition
- PMID: 17363894
- PMCID: PMC1852776
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601650
Granzyme H destroys the function of critical adenoviral proteins required for viral DNA replication and granzyme B inhibition
Abstract
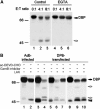
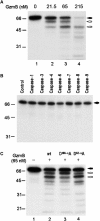
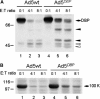
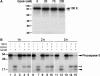
Granzymes are key components of the immune response that play important roles in eliminating host cells infected by intracellular pathogens. Several granzymes are potent inducers of cell death. However, whether granzymes use additional mechanisms to exert their antipathogen activity remains elusive. Here, we show that in adenovirus-infected cells in which granzyme B (gzmB) and downstream apoptosis pathways are inhibited, granzyme H (gzmH), an orphan granzyme without known function, directly cleaves the adenovirus DNA-binding protein (DBP), a viral component absolutely required for viral DNA replication. We directly addressed the functional consequences of the cleavage of the DBP by gzmH through the generation of a virus that encodes a gzmH-resistant DBP. This virus demonstrated that gzmH directly induces an important decay in viral DNA replication. Interestingly, gzmH also cleaves the adenovirus 100K assembly protein, a major inhibitor of gzmB, and relieves gzmB inhibition. These results provide the first evidence that granzymes can mediate antiviral activity through direct cleavage of viral substrates, and further suggest that different granzymes have synergistic functions to outflank viral defenses that block host antiviral activities.
Figures


References
-
- Andrade F, Bull HG, Thornberry NA, Ketner GW, Casciola-Rosen LA, Rosen A (2001) Adenovirus L4-100K assembly protein is a granzyme B substrate that potently inhibits granzyme B-mediated cell death. Immunity 14: 751–761 - PubMed
-
- Andrade F, Casciola-Rosen LA, Rosen A (2004) Granzyme B-induced cell death. Acta Haematol 111: 28–41 - PubMed
-
- Andrade F, Roy S, Nicholson D, Thornberry N, Rosen A, Casciola-Rosen L (1998) Granzyme B directly and efficiently cleaves several downstream caspase substrates: implications for CTL-induced apoptosis. Immunity 8: 451–460 - PubMed
-
- Asselbergs FA, Smart JE, Mathews MB (1983) Analysis of expression of adenovirus DNA (fragments) by microinjection in Xenopus oocytes. Independent synthesis of minor early region 2 proteins. J Mol Biol 163: 209–238 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

