Dynorphin activates quorum sensing quinolone signaling in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 17367209
- PMCID: PMC1828698
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030035
Dynorphin activates quorum sensing quinolone signaling in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Erratum in
- PLoS Pathog. 2007 May;3(5):e67. Petroff, Elaine [corrected to Petrof, Elaine O]
Abstract
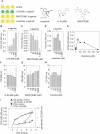
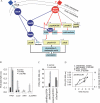
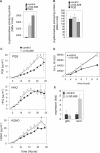
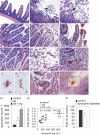
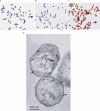
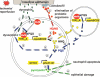
There is now substantial evidence that compounds released during host stress directly activate the virulence of certain opportunistic pathogens. Here, we considered that endogenous opioids might function as such compounds, given that they are among the first signals to be released at multiple tissue sites during host stress. We tested the ability of various opioid compounds to enhance the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa using pyocyanin production as a biological readout, and demonstrated enhanced virulence when P. aeruginosa was exposed to synthetic (U-50,488) and endogenous (dynorphin) kappa-agonists. Using various mutants and reporter strains of P. aeruginosa, we identified involvement of key elements of the quorum sensing circuitry such as the global transcriptional regulator MvfR and the quorum sensing-related quinolone signaling molecules PQS, HHQ, and HQNO that respond to kappa-opioids. The in vivo significance of kappa-opioid signaling of P. aeruginosa was demonstrated in mice by showing that dynorphin is released from the intestinal mucosa following ischemia/reperfusion injury, activates quinolone signaling in P. aeruginosa, and enhances the virulence of P. aeruginosa against Lactobacillus spp. and Caenorhabditis elegans. Taken together, these data demonstrate that P. aeruginosa can intercept opioid compounds released during host stress and integrate them into core elements of quorum sensing circuitry leading to enhanced virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Dawkins R. The selfish gene. 3rd edition. New York: Oxford University Press; 2006. 384
-
- Wu L, Estrada O, Zaborina O, Bains M, Shen L, et al. Recognition of host immune activation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Science. 2005;309:774–777. - PubMed
-
- Porat R, Clark BD, Wolff SM, Dinarello CA. Enhancement of growth of virulent strains of Escherichia coli by interleukin-1. Science. 1991;254:430–432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

