The evolution of amphibian metamorphosis: insights based on the transformation of the aortic arches of Pelobates fuscus (Anura)
- PMID: 17367494
- PMCID: PMC2100297
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2007.00710.x
The evolution of amphibian metamorphosis: insights based on the transformation of the aortic arches of Pelobates fuscus (Anura)
Abstract
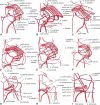
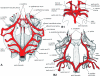
In order to gain insights into how the aortic arches changed during the transition of vertebrates to land, transformations of the aortic arches during the metamorphosis of Pelobates fuscus were investigated and compared with data from the early development of a recent ganoid fish Amia calva and a primitive caudate amphibian Salamandrella keyserlingi. Although in larval Pelobates, as in other non-pipid anurans, the gill arches serve partly as a filter-feeding device, their aortic arches maintain the original piscine-like arrangement, except for the mandibular and hyoid aortic arches which were lost. As important pre-adaptations for breathing of atmospheric oxygen occur in larval Pelobates (which have well-developed, though non-respiratory lungs and pulmonary artery), transformation of aortic arches during metamorphosis is fast. The transformation involves disappearance of the ductus Botalli, which results in a complete shunting of blood into the lungs and skin, disappearance of the ductus caroticus, which results in shunting of blood into the head through the arteria carotis interna, and disappearance of arch V, which results in shunting blood to the body through arch IV (systemic arch). It is supposed that the branching pattern of the aortic arches of permanently water-dwelling piscine ancestors, of intermediate forms which occasionally left the water and of primitive tetrapods capable of spending longer periods of time on land had been the same as in the prematamorphic anuran larvae or in some metamorphosed caudates in which the ductus caroticus and ductus Botalli were not interrupted, and arch V was still complete.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mandibular arch musculature of anuran tadpoles, with comments on homologies of amphibian jaw muscles.J Morphol. 2001 Jan;247(1):1-33. doi: 10.1002/1097-4687(200101)247:1<1::AID-JMOR1000>3.0.CO;2-3. J Morphol. 2001. PMID: 11124683
-
Restructuring of the Optokinetic Reflex during Metamorphosis in Pelobates fuscus Laur.Dokl Biol Sci. 2022 Oct;506(1):132-136. doi: 10.1134/S0012496622050064. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Dokl Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36301419
-
The evolution of larvae in temnospondyls and the stepwise origin of amphibian metamorphosis.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2024 Oct;99(5):1613-1637. doi: 10.1111/brv.13084. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2024. PMID: 38599802 Review.
-
Breathing air in air: in what ways might extant amphibious fish biology relate to prevailing concepts about early tetrapods, the evolution of vertebrate air breathing, and the vertebrate land transition?Physiol Biochem Zool. 2004 Sep-Oct;77(5):720-31. doi: 10.1086/425184. Physiol Biochem Zool. 2004. PMID: 15547791
-
[Evolutionary transformations of ontogenesis in anuran amphibians].Ontogenez. 2004 May-Jun;35(3):165-70. Ontogenez. 2004. PMID: 15334818 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Sonic hedgehog is required for the assembly and remodeling of branchial arch blood vessels.Dev Dyn. 2008 Jul;237(7):1923-34. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21608. Dev Dyn. 2008. PMID: 18570256 Free PMC article.
-
Morphogenetic processes in the development and evolution of the arteries of the pharyngeal arches: their relations to congenital cardiovascular malformations.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Oct 12;11:1259175. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1259175. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37900278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aichhorn H, Lametschwandtner A. Vascular regression during the amphibian metamorphosis – a scanning electron microscope study of vascular corrosion cast of the ventral velum in tadpoles of Xenopus laevis Daudin. Scanning. 1996;18:447–455. - PubMed
-
- Baker CL. The comparative anatomy of the aortic arches of the urodeles and their relation to respiration and degree of metamorphosis. J Tennessee Acad Sci. 1949;24:12–40.
-
- Balinsky BI. An Introduction to Embryology. 5. Philadelphia: Saunders College Publishing; 1981.
-
- Bartel H, Lametschwandtner A. Intussusceptive microvasculant growth in the lung of larval Xenopus laevis. A light microscope, transmission electron microscope and SEM study of microvascular corrosion casts. Anat Embryol. 2000;202:55–66. - PubMed
-
- Bjerring HC. Does a homology exist between the basicranial muscle and the polar cartilage? Colloques int Cent Natn Rech Scient. 1967;163:223–267.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

