Expression of RhoA by inflammatory macrophages and T cells in rat experimental autoimmune neuritis
- PMID: 17367505
- PMCID: PMC4401224
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00004.x
Expression of RhoA by inflammatory macrophages and T cells in rat experimental autoimmune neuritis
Abstract
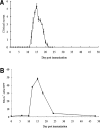
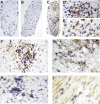
RhoA is one of the best-studied members of Rho GTPases. Experimental autoimmune neuritis (EAN), which is characterized by infiltration of T cells and macrophages into the peripheral nervous system, is an autoantigen-specific T-cell-mediated animal model of human Guillain-Barré Syndrome. In this study, RhoA expression has been investigated in the dorsal/ventral roots of EAN rats by immunohistochemistry. A significant accumulation of RhoA+ cells was observed on Day 12, with a maximum around Day 15, correlating to the clinical severity of EAN. In dorsal/ventral roots of EAN, RhoA+ cells were seen in perivascular areas but also in the parenchyma. Furthermore, double-labelling experiments showed that the major cellular sources of RhoA were reactive macrophages and T cells. In conclusion, this is the first demonstration of the presence of RhoA in the dorsal/ventral roots of EAN. The time courses and cellular sources of RhoA together with the functions of RhoA indicate that RhoA may function to facilitate macrophage and T-cell infiltration in EAN and therefore could be a potential therapeutic target.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of experimental autoimmune neuritis in Lewis rats: the dual role of macrophages.Histol Histopathol. 2013 Jun;28(6):679-84. doi: 10.14670/HH-28.679. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Histol Histopathol. 2013. PMID: 23440744 Review.
-
Distribution of inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the peripheral nervous system of Lewis rats during ascending paresis and spontaneous recovery from experimental autoimmune neuritis.Neuroimmunomodulation. 2010;17(1):56-66. doi: 10.1159/000243086. Epub 2009 Oct 5. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2010. PMID: 19816058
-
Inhibition of experimental autoimmune neuritis by an antibody to the lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1.Lab Invest. 1994 May;70(5):667-75. Lab Invest. 1994. PMID: 8196363
-
Expression of interleukin-16 in sciatic nerves, spinal roots and spinal cords of experimental autoimmune neuritis rats.Brain Pathol. 2009 Apr;19(2):205-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2008.00172.x. Epub 2008 May 6. Brain Pathol. 2009. PMID: 18462471 Free PMC article.
-
Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg cytokines in Guillain-Barré syndrome and experimental autoimmune neuritis.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Oct;24(5):443-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.05.005. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 23791985 Review.
References
-
- Izumo S, Linington C, Wekerle H, Meyermann R. Morphologic study on experimental allergic neuritis mediated by T cell line specific for bovine P2 protein in Lewis rats. Lab Invest. 1985;53:209–18. - PubMed
-
- Linington C, Izumo S, Suzuki M, Uyemura K, Meyermann R, Wekerle H. A permanent rat T cell line that mediates experimental allergic neuritis in the Lewis rat in vivo. J Immunol. 1984;133:1946–50. - PubMed
-
- Maurer M, Gold R. Animal models of immune-mediated neuropathies. Curr Opin Neurol. 2002;15:617–22. - PubMed
-
- Shin HC, McFarlane EF, Pollard JD, Watson EG. Induction of experimental allergic neuritis with synthetic peptides from myelin P2 protein. Neurosci Lett. 1989;102:309–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

