The role of the purinergic P2X7 receptor in inflammation
- PMID: 17367517
- PMCID: PMC1838907
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-9255-4-5
The role of the purinergic P2X7 receptor in inflammation
Abstract
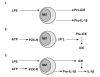
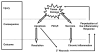
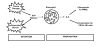
The inflammatory process, orchestrated against a variety of injurious stimuli, is composed of three inter-related phases; initiation, propagation and resolution. Understanding the interplay between these three phases and harnessing the beneficial properties of inflammation whilst preventing its damaging effects, will undoubtedly lead to the advent of much needed therapies, particularly in chronic disease states. The P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) is increasingly recognised as an important cell surface regulator of several key inflammatory molecules including IL-1beta, IL-18, TNF-alpha and IL-6. Moreover, as P2X7R-dependent cytokine production is driven by activating the inflammasome, antagonists of this receptor are likely to have therapeutic potential as novel anti-inflammatory therapies. The function of the P2X7R in inflammation, immunity and its potential role in disease will be reviewed and discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Abbracchio MP, Boeynaems JM, Barnard EA, Boyer JL, Kennedy C, Miras-Portugal MT, King BF, Gachet C, Jacobson KA, Weisman GA, Burnstock G. Characterization of the UDP-glucose receptor (re-named here the P2Y14 receptor) adds diversity to the P2Y receptor family. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 2003;24:52–55. doi: 10.1016/S0165-6147(02)00038-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- North RA. Molecular Physiology of P2X Receptors. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:1013–1067. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

