Cryospray ablation (CSA) in the palliative treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus
- PMID: 17367523
- PMCID: PMC1845148
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7819-5-34
Cryospray ablation (CSA) in the palliative treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus
Abstract
Background: Esophageal carcinoma is the ninth most prevalent cancer worldwide with squamous cell carcinoma (SCCA) and adenocarcinoma accounting for the vast majority of new cases (13,900 in 2003). Cure rates in the U.S. are less than 10%, similar to lung cancer. More than 50% of patients with esophageal carcinoma present with unresectable or metastatic disease, are not surgical candidates, or display disease progression despite the addition of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy to surgery. Need for improved palliation exits.
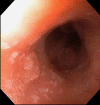
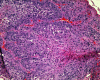
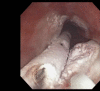
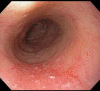
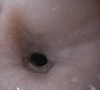
Case presentation: This case describes a 73-year-old African American male who presented with recurrent squamous cell carcinoma (SCCA) of the esophagus who has a achieved complete remission for 24 months via endoscopic cryospray ablation.
Conclusion: Endoscopic cryo spray ablation warrants further investigation as a palliative treatment modality for esophageal cancer. This is the first reported case in the medical literature.
Figures
References
-
- Sun W, Haller D. Oncology:VI Pancreatic, gastric and other gastrointestinal cancers. In: Dale DC, Federman DD, editor. ACP Medicine. WebMD Inc; 2004.
-
- Jemal A, Murray T, Samuels A, Ghafoor A, Ward E, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2003. CA Cancer J Clin. 2003;53:5–26. - PubMed
-
- Posner MC, Forastiere AA, Minsky BD. Cancer of the Esophagus. In: Devita, Vt, Hellman, S, Rosenberg, SA, editor. Cancer: Principles & Practice of Oncology. 7. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

